The right first aid for Quincke's edema


Eva Zakharova
Quincke's edema: first aid and recommendations
One of the most common questions in allergology is: "Quincke's edema what is it?" It is this condition, its symptoms and first aid that we will talk about in this article.
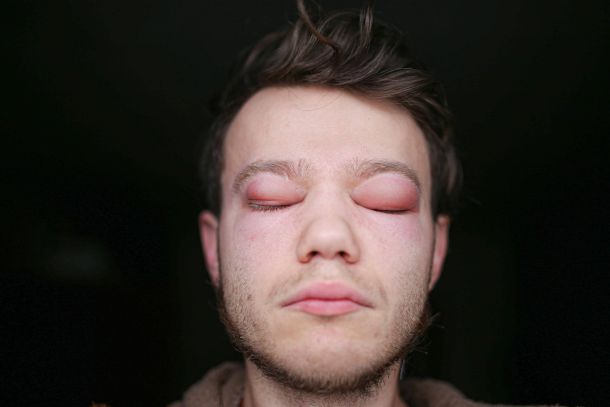
Quincke's edema, also known as angioedema, is the body's sharp reaction to an allergen, causing tissue swelling, most commonly on the face. This condition can be seriously life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
Causes and symptoms of Quincke's edema

The cause of Quincke's edema is often contact with an allergen. This can be food, medications, insect bites, and physical factors such as cold or stress. Symptoms of Quincke's edema include rapidly developing swelling of the face, hands, feet, or genitals, sometimes accompanied by itching or redness. Adults may also experience abdominal pain or a feeling of tightness in the chest.
Dangers and complications of Quincke's edema
The main danger of Quincke's edema is the possibility of swelling of the airways, which can lead to suffocation. Other possible complications are anaphylactic shock and loss of consciousness.
First aid for Quincke's edema
If you are faced with Quincke's edema, it is important to know how to relieve the swelling and what to do at home before the ambulance arrives.
- The first course of action for Quincke's edema is to stop contact with the suspected allergen.
- If anti-allergy medications such as Suprastin, Dimedrol or Erius are available, they should be taken immediately. An injection of glucocorticoids, such as Prednisolone, may also be helpful.
- Applying cold compresses to swollen areas may help reduce swelling and ease discomfort.
- Try to avoid further irritation of the swollen skin through rubbing or scratching.
When should you seek medical attention?
No matter what first aid you provide at home, you should seek medical attention at the first signs of Quincke's edema. This is especially important if the swelling continues to worsen or spread.
If the adult has trouble breathing or swallowing, this signals the seriousness of the condition and the need for emergency medical attention.
Anaphylactic shock and its signs
Anaphylactic shock is a life-threatening condition that requires emergency care. Signs include profuse sweat, pale skin, rapid pulse, and loss of consciousness.
Prevention of Quincke's edema

Preventing Quincke's edema includes avoiding contact with allergens and taking regular anti-allergy medications as prescribed by your doctor. Patients who have already had Quincke's edema should always carry epinephrine (adrenaline) for emergency self-administration.
In conclusion, we would like to emphasize that Quincke's edema is a serious condition that requires emergency care. Understanding its symptoms and knowing first aid can save a life. If you suspect Quincke's edema, seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Improving your awareness of the condition, its signs, emergency home care for Quincke's edema, and taking necessary medications in general increases your chances of a quick recovery and avoiding possible dangerous complications.
It is important to remember that the best prevention is to identify and avoid allergens. Be vigilant and respect your health and the health of your loved ones. At the slightest suspicion of Quincke's edema, do not hesitate to seek professional medical attention. Remember that a quick reaction and the right first aid can save a life.
New materials
Popular Articles
We recommend reading
Contact us in the Contact Us section to ask questions, offer ideas, or for more information about our allergy resource.
Our articles are your trusted source of allergy knowledge. Learn how to make life with allergic reactions easier on our specialized portal.
©
Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
© Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
The information on this site is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. We recommend consulting with qualified medical professionals for accurate information and advice.
 English
English  Українська
Українська  Русский
Русский