Bee sting allergy: causes, symptoms and treatment


Viktor Levchenko
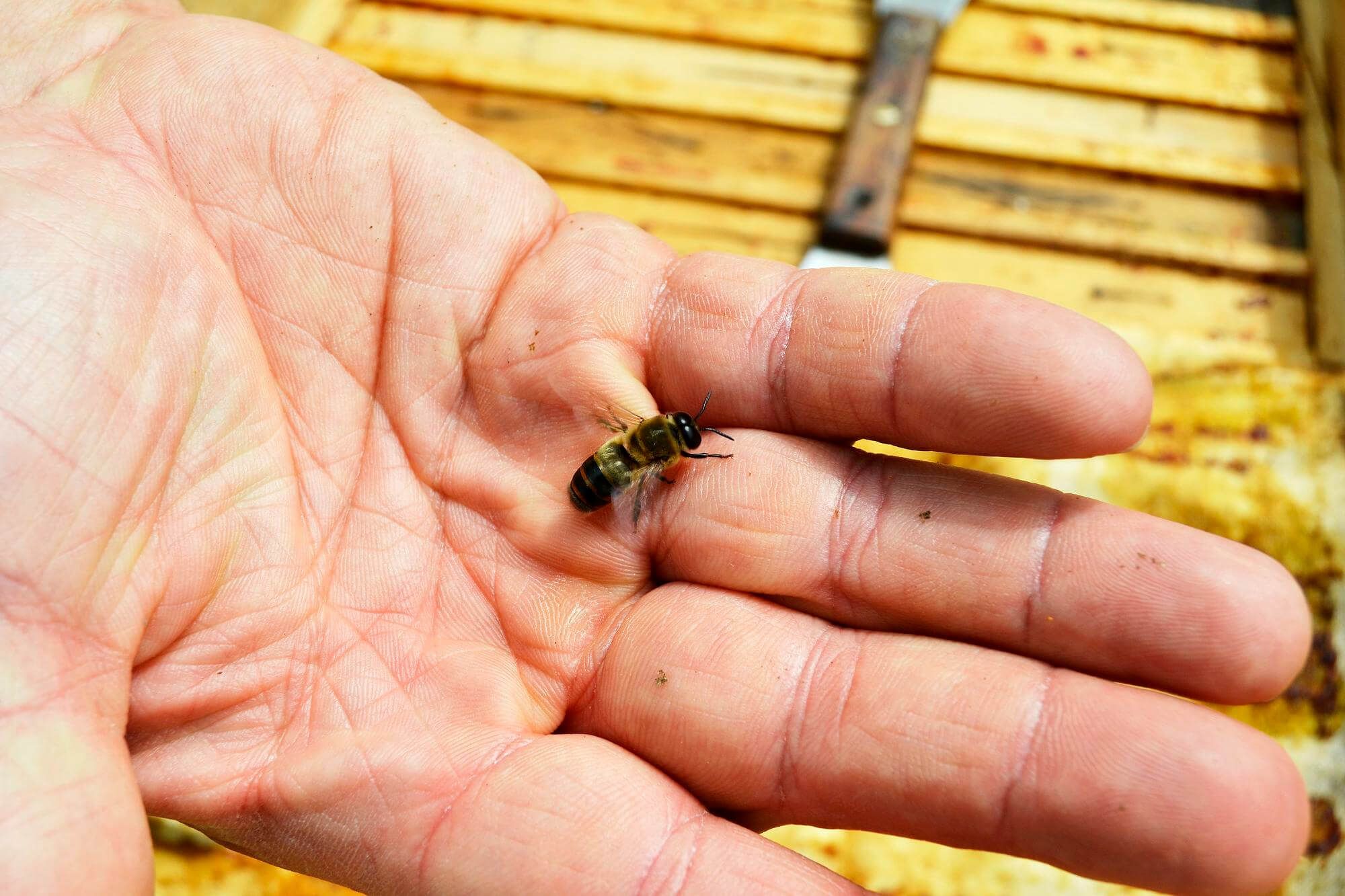
A bee sting allergy is the body's immune response to bee venom, which can present various symptoms and cause serious complications. It is important to know what signs indicate an allergic reaction and what to do if it occurs.
Causes of an allergic reaction to a bee sting
A bee sting allergy occurs when a person's immune system reacts to the proteins in bee venom as harmful substances. This results in the production of antibodies and the release of substances that cause the allergic reaction.
Bee venom consists of various proteins, amino acids, enzymes and peptides. In particular, phospholipase A2 is one of the major allergens that cause allergies to bee stings.
Bee sting allergy symptoms
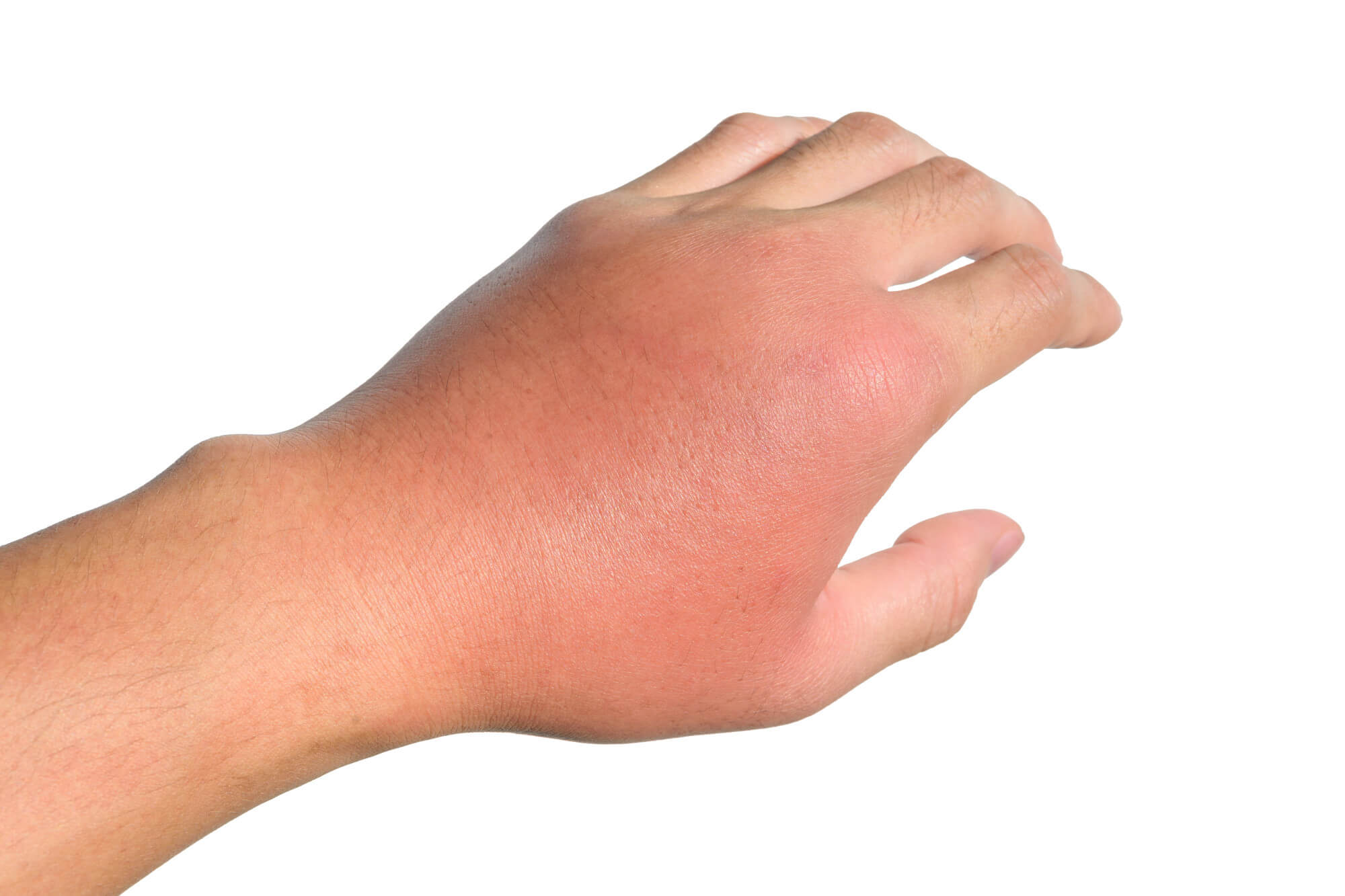
- After a bee sting, swelling and redness of the skin may occur at the site of the sting. Usually such manifestations are harmless and go away after a few hours or days.
- In addition to swelling and redness, after a bee sting, there may be itching and soreness in the area of the sting. This is also a local reaction to a bee sting and usually goes away on its own.
- In some people, bee sting allergy can cause urticaria, a rash accompanied by itching. In more severe cases, Quincke's edema can develop, in which swelling occurs in the deeper layers of the skin and mucous membranes, causing a life-threatening situation due to possible breathing difficulties.
- An allergic reaction to a bee sting can cause bronchospasm - a narrowing of the bronchi that leads to difficulty breathing and shortness of breath. This condition requires immediate medical attention.
- The most dangerous manifestation of an allergy to a bee sting is anaphylactic shock, which can develop within minutes after the sting. Symptoms of anaphylactic shock include dizziness, decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, vomiting, and loss of consciousness.
Bee sting allergy treatment

When a bee sting occurs, the sting should be removed as quickly as possible to prevent further absorption of the venom. The sting should then be cooled using ice or a cold compress to help reduce swelling and pain.
Antihistamines such as loratadine, cetirizine, or diphenhydramine can be taken to reduce the allergic reaction. They can help reduce itching, swelling, and other symptoms of bee sting allergy.
Medical treatment for bee sting allergy
If severe allergic reactions develop, such as anaphylactic shock or Quincke's edema, medical attention should be sought immediately. Doctors may administer adrenaline, which relieves bronchospasm and stabilizes blood pressure, and glucocorticoids, such as prednisolone, to reduce inflammation.
Immunotherapy and desensitization
Immunotherapy can be used to prevent bee sting allergy in particularly sensitive people. This is a long-term course of treatment in which small doses of bee venom are administered to the patient, gradually increasing. This approach allows the body to adapt to the allergen and reduce the risk of developing a severe allergic reaction to a bee sting in the future.
In conclusion, bee sting allergies can manifest with a variety of symptoms, from mild local reactions to life-threatening conditions such as anaphylactic shock or Quincke's edema. It is important to know how to provide first aid for a bee sting and when to seek medical attention. In some cases, immunotherapy can help prevent severe allergic reactions to a bee sting and improve allergy sufferers' quality of life.
New materials
Popular Articles
We recommend reading
Contact us in the Contact Us section to ask questions, offer ideas, or for more information about our allergy resource.
Our articles are your trusted source of allergy knowledge. Learn how to make life with allergic reactions easier on our specialized portal.
©
Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
© Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
The information on this site is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. We recommend consulting with qualified medical professionals for accurate information and advice.
 English
English  Українська
Українська  Русский
Русский