Fungal allergy: how to avoid problems?


Eva Zakharova
Mushroom allergy is a fairly common problem, especially in the warm season when the season for collecting and consuming various types of mushrooms begins. In this article, we will discuss the symptoms, causes, treatment, and prevention methods of mushroom allergy.
Types of mushroom allergy
Mushroom allergy can manifest itself in different forms. It can be food-related, when allergy occurs to mushrooms such as champignons, white mushrooms, chanterelles, morels, and other types of mushrooms that are consumed as food. Allergy can also be contact-related when a person comes into contact with mushrooms in nature or during their collection and processing.
Symptoms of mushroom allergy
Mushroom allergy can manifest itself in various symptoms. The way mushroom allergy manifests itself depends on individual characteristics of the body. Among the most common symptoms are:
- skin rash, itching, redness;
- swelling, especially of the face and upper respiratory tract;
- runny nose, nasal congestion, sneezing;
- itching and tearing of the eyes;
- respiratory problems, including shortness of breath and bronchospasms;
- gastrointestinal disorders such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
Causes of mushroom allergy

The causes of mushroom allergy are related to an individual's predisposition to allergic reactions. Mushrooms contain various proteins and other substances that can cause allergies in some people. Does everyone have a mushroom allergy? The answer is no, mushroom allergy only develops in those who have a genetic predisposition to allergic reactions.
Common types of mushrooms that cause allergies
Mushroom allergy can be caused by different types of mushrooms. Some of the most commonly allergenic mushrooms include:
- Champignons are one of the most popular types of mushrooms consumed as food, and many people experience allergy to champignons. They can cause allergic reactions both when in contact with the skin and when consumed as food.
- White mushrooms can also cause allergies in some people. They contain specific allergens that can lead to allergic reactions when in contact or when consumed as food.
- Chanterelles are also popular edible mushrooms that can cause allergies in some people. Allergy to chanterelles can manifest itself both when in contact with mushrooms and when consumed as food.
- Morels are another type of mushroom that can cause allergic reactions. Allergy to morels can occur when in contact with the skin or when consumed as food.
- In addition to the above-mentioned types, mushroom allergy can be caused by other types of mushrooms such as porcini, shiitake, truffles, etc.
Diagnosis of mushroom allergy
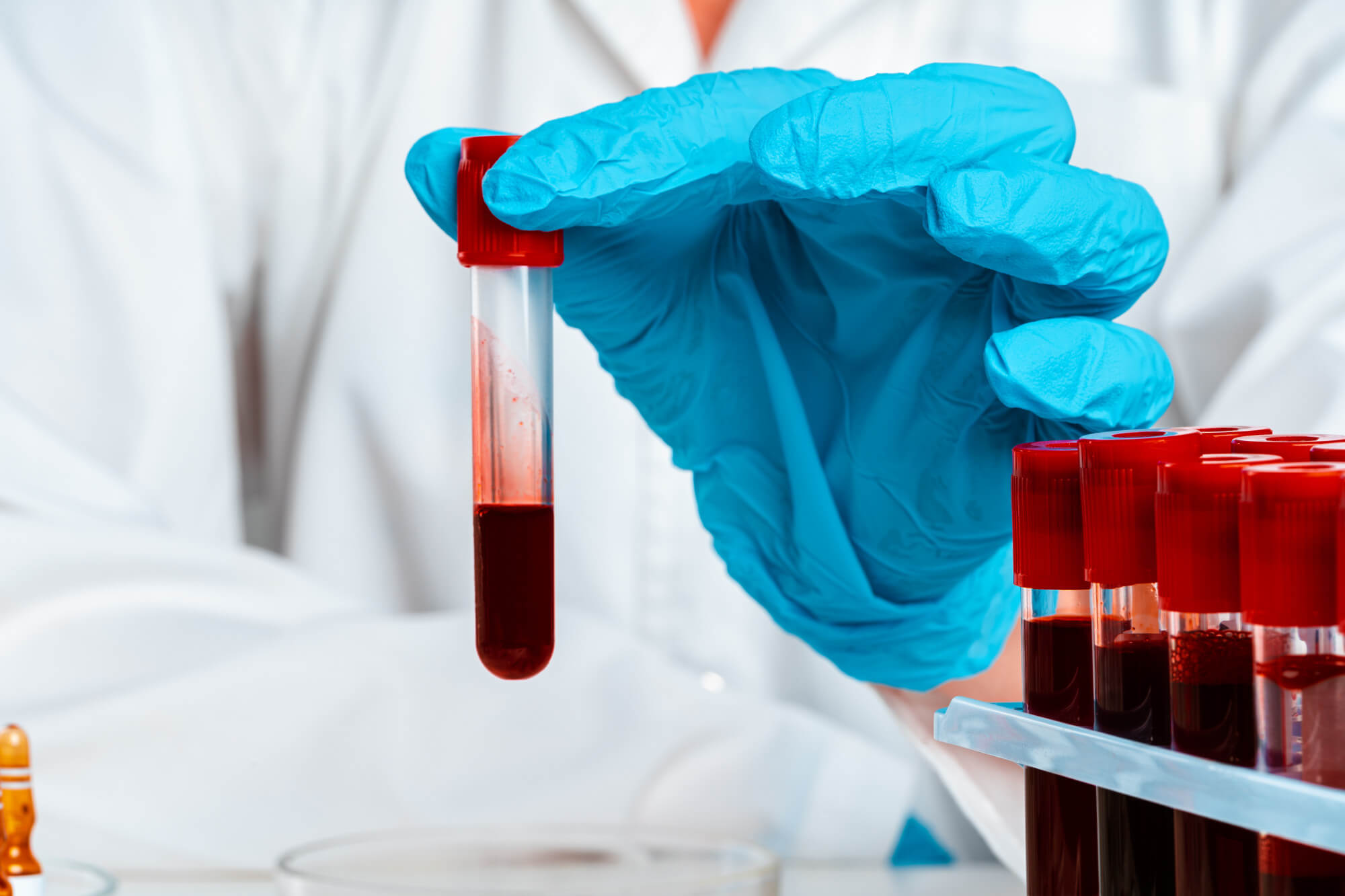
Various methods of investigation are used for accurate diagnosis of mushroom allergy:
- Specific tests, such as a blood test for antibodies to mushroom allergens, can help determine the presence of allergy to specific types of mushrooms. This can help the doctor determine which mushrooms are causing the allergic reaction and develop an individual treatment plan.
- Skin tests can also be used to determine allergy to mushrooms. During a skin test for mushroom allergy, the allergen (mushroom extract) is applied to the skin, and the skin reaction is observed. If redness and itching occur, this may indicate the presence of allergy to mushrooms.
- Blood tests, such as a complete blood count and determination of immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels, can provide additional information on the presence of mushroom allergy and the severity of symptoms.
Treatment of mushroom allergy
Treatment of mushroom allergy includes various methods aimed at reducing allergy symptoms and improving the patient's quality of life.
Antihistamines, such as loratadine, cetirizine, and fexofenadine, may be prescribed by a doctor to relieve itching, rash, and other symptoms of mushroom allergy. They block the action of histamine, a substance that causes allergic symptoms.
Corticosteroids such as hydrocortisone and prednisolone may be used to relieve inflammation and itching in mushroom allergy. They can be prescribed in the form of ointments, creams, or tablets depending on the severity of the allergic reaction and the location of the affected area.
Immunotherapy
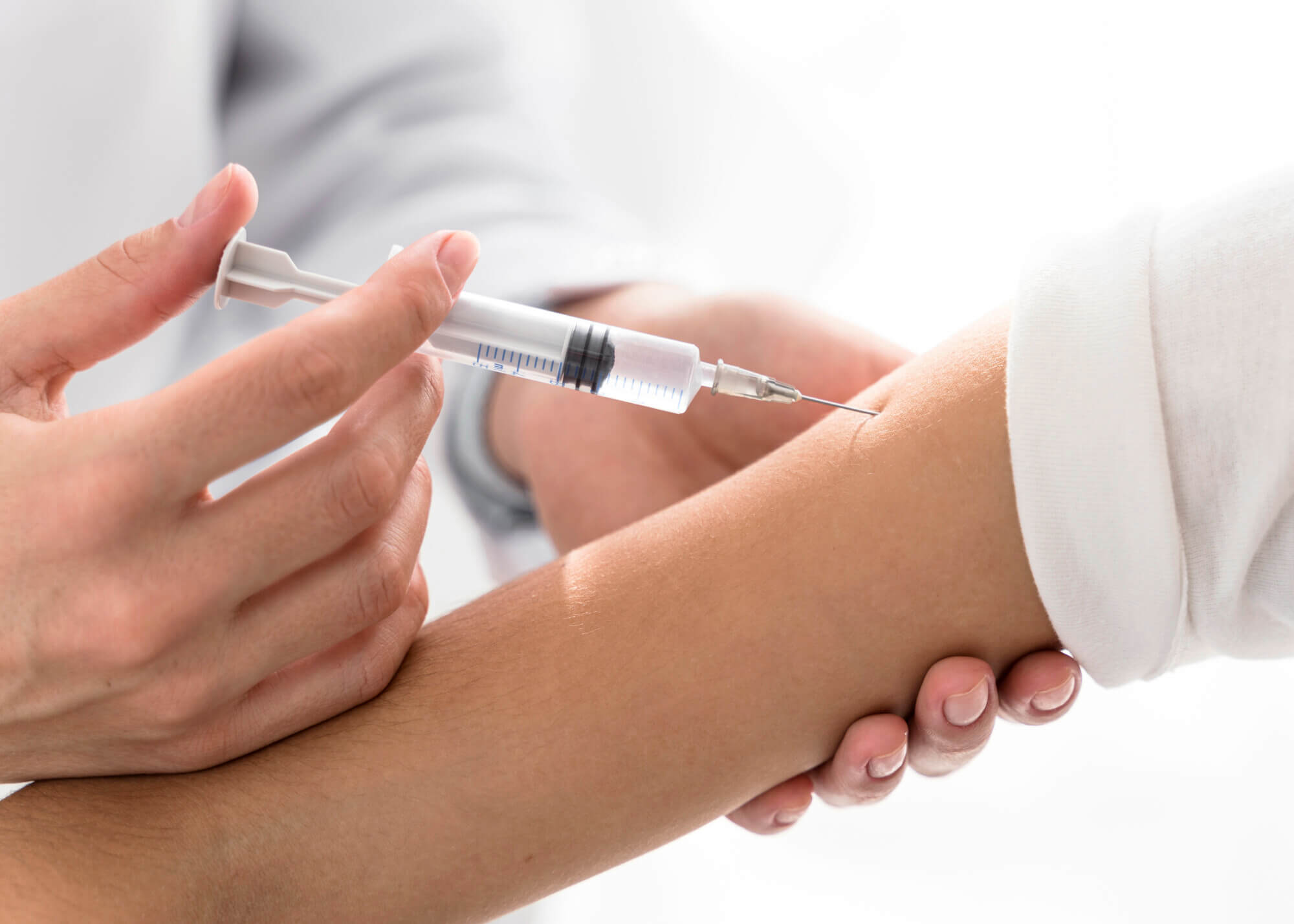
Immunotherapy may be used to treat mushroom allergy in some patients. This treatment method involves gradually introducing the allergen (mushroom extract) into the body in order to develop immune tolerance to it. Immunotherapy is conducted under strict medical supervision and may take several months or even years.
Prevention of mushroom allergy
To prevent mushroom allergy, it is recommended to follow a number of simple rules:
- Observing the rules of storage and preparation of mushrooms can reduce the risk of developing an allergy. Mushrooms should be thoroughly washed, processed, and cooked before consumption.
- If you are already known to be allergic to certain types of mushrooms, try to avoid contact with them. Avoid eating allergenic mushrooms and avoid contact with them in nature.
Allergy to mushrooms is a common phenomenon, which can cause a variety of symptoms and reduce patients' quality of life. However, with timely diagnosis and proper treatment, you can significantly alleviate the patient's condition and prevent the development of serious complications. If you suspect that you suffer from mushroom allergy, be sure to see an allergist for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
New materials
Popular Articles
We recommend reading
Contact us in the Contact Us section to ask questions, offer ideas, or for more information about our allergy resource.
Our articles are your trusted source of allergy knowledge. Learn how to make life with allergic reactions easier on our specialized portal.
©
Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
© Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
The information on this site is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. We recommend consulting with qualified medical professionals for accurate information and advice.
 English
English  Українська
Українська  Русский
Русский