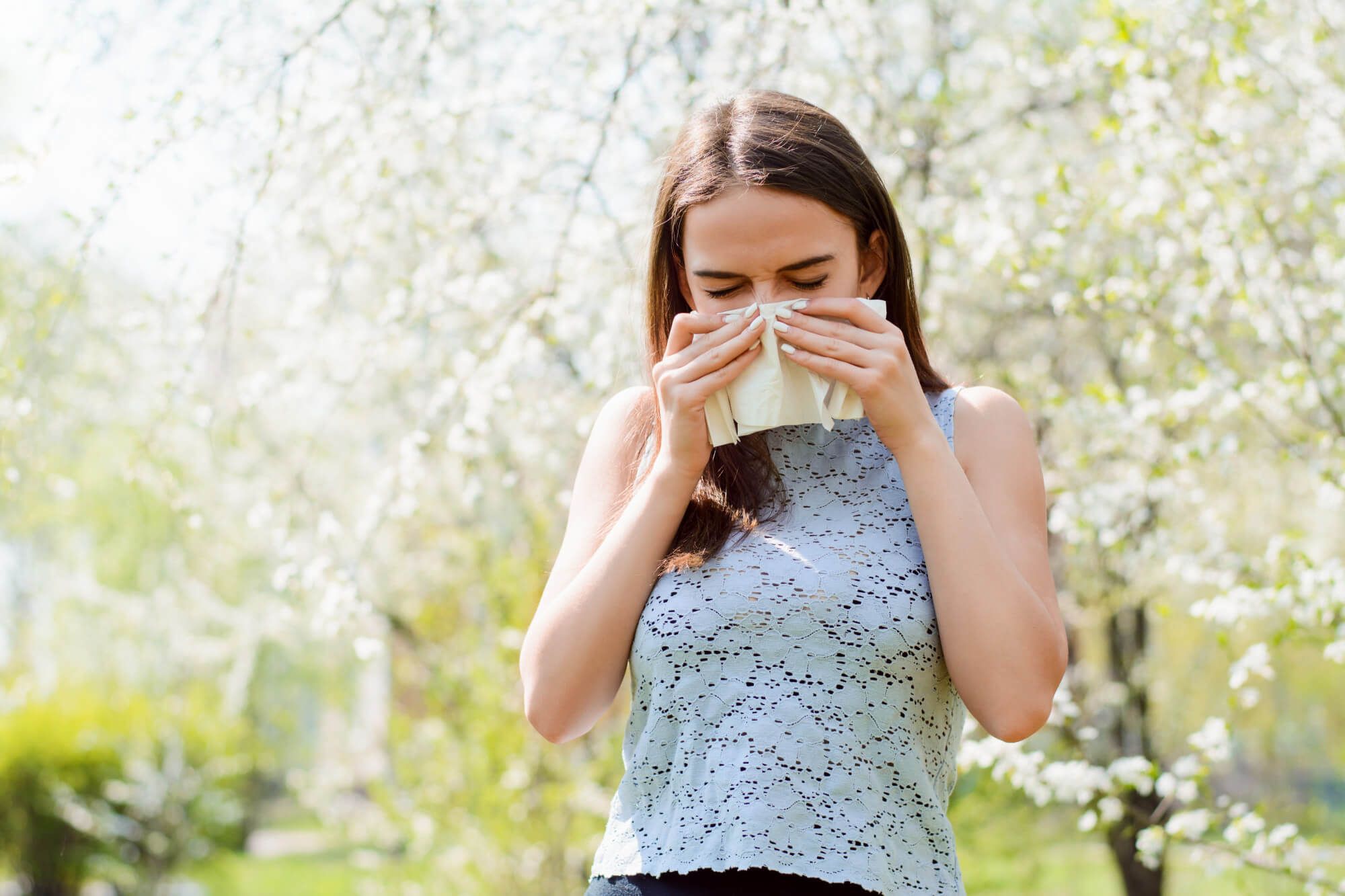
How to recognize cross-allergies: signs and symptoms


Eva Zakharova
Cross-allergies are a common problem among allergy sufferers. In this comprehensive guide from an experienced allergist, you'll learn all about cross-allergies, their causes, common allergen groups, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
What is a cross-allergy?
A cross-allergy is a condition in which the body reacts to different allergens that share common structural characteristics. As a result, a person becomes sensitive to several different foods, pollens, or other substances that have similar antigens.
Causes of cross-allergies
One factor that influences the development of cross-allergies is genetic predisposition. Heredity plays a key role in the occurrence of allergies, including cross-allergies.
The second important factor is the relationship to the environment. Frequent contact with allergens and unfavorable environmental conditions can contribute to the development of allergies, including cross-allergies.
Common cross-allergen groups
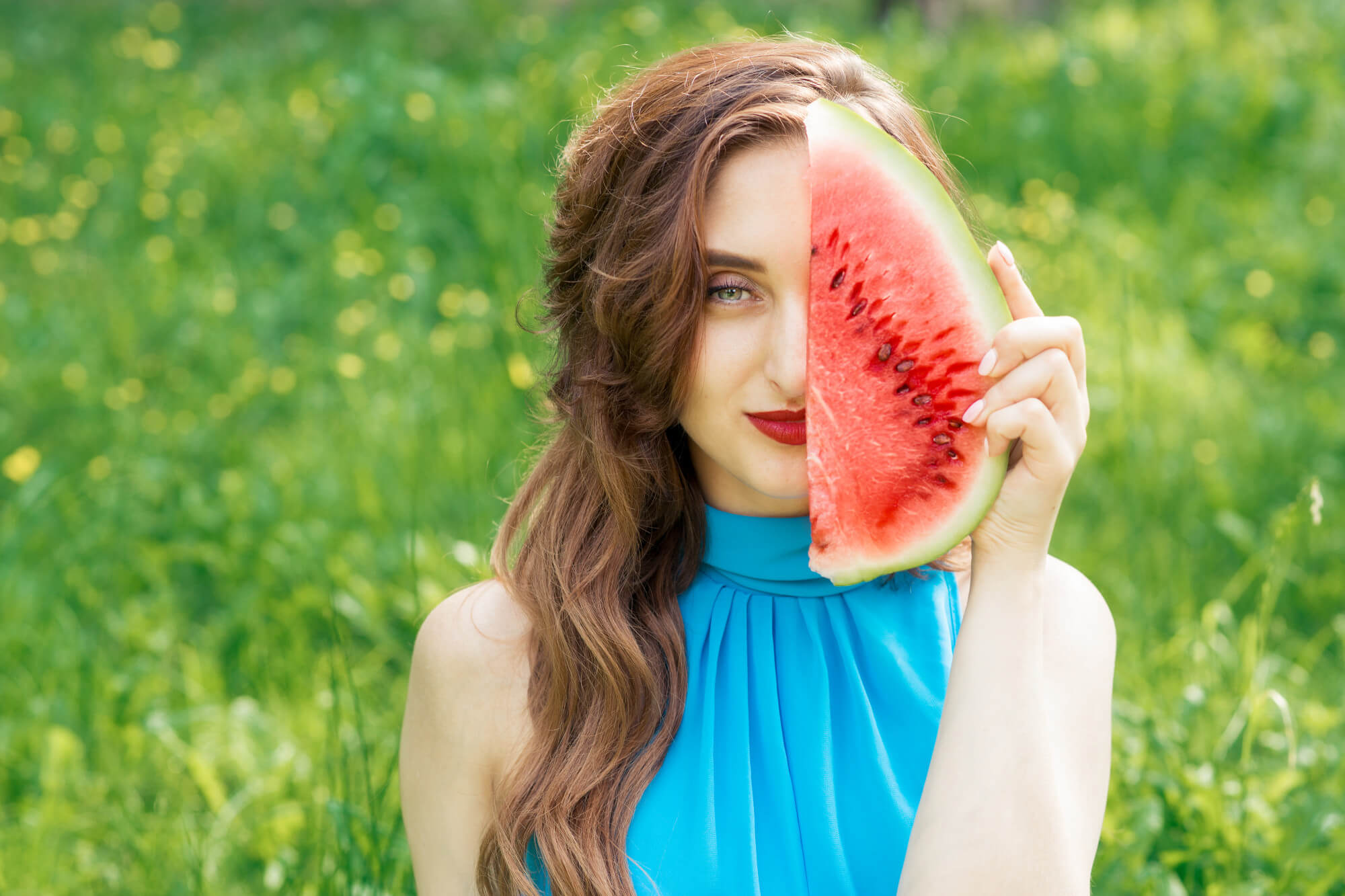

Food cross-allergies
Cross-allergies to fruits and vegetables are usually associated with reactions to pollen. For example, apple and birch pollen allergies share common allergens. The cross-allergy chart shows links between different foods and pollen.
| Main allergen | Associated foods and allergens |
| Birch pollen | Apples, pears, cherries, peaches, apricots, mangoes, nuts, carrots |
| Ambrosia pollen | Watermelon, melon, bananas, sunflowers, camomile, eucalyptus, nectarines |
| Maple pollen | Tree fruits (oranges, mandarins, lemons) |
| Latex pollen | Avocados, bananas, kiwi, papaya, mulberries, tomatoes |
| Pollen from grasses | Bread, cereals, honey, flour, beer, sunflower seeds |
Nut and seed allergies can cause cross-allergic reactions with other foods or pollens. For example, a walnut allergy may be accompanied by a hazelnut allergy.
Cross-allergies between dairy products and meat are less common. However, some people may have allergic reactions to cow's milk and beef.
Cross-allergies to pollen and plants
Cross-allergies to trees and shrubs are usually related to pollen allergies to these plants. For example, an allergy to birch pollen can cause a reaction to apples or nuts.
Allergies to grass and flower pollen can also cause cross-allergic reactions. Often allergies to pollen from different types of grasses cause reactions to foods that contain proteins structurally similar to pollen allergens.
Diagnosis and treatment of cross-allergy

The first step in diagnosing cross-allergy is to take a history. The doctor asks the patient questions about the symptoms, the products causing the reaction, and the history of allergies in the family.
- Skin tests are used to determine the specific allergens causing the reaction. This involves applying an allergen solution to the skin and observing the reaction.
- Immunological tests, such as determination of specific IgE antibody levels, can help in identifying allergens and confirming the diagnosis of cross-allergy.
Basic approaches to cross-allergy treatment
The basis of cross-allergy treatment is avoidance of contact with allergens. The doctor will make an individualized plan to eliminate problematic foods or substances from the patient's environment.
Treatment of cross-allergy symptoms often includes the use of antihistamines such as loratadine, cetirizine, or fexofenadine. In some cases, corticosteroids or mastocyte-stabilizing drugs (e.g., ketotifen) may be prescribed.
Immunotherapy is a method of treatment in which small doses of an allergen are given to the patient on a regular basis to gradually desensitize the body to it. This method is used for some forms of cross-allergies, especially those associated with pollen allergies.
Tips and advice for cross-allergy prevention
To prevent the development of cross-allergies, it is important to follow a number of simple rules:
- See your allergist in time if you suspect an allergy.
- Follow your doctor's recommendations to eliminate allergens from your diet or environment.
- Regularly hygienize your home, especially during plant blooms.
- Avoid contact with pets if they are a source of allergy.
- Monitor your health and have regular medical check-ups.
Cross-allergy is a complex phenomenon, requiring a careful approach to diagnosis and treatment. Seeing your doctor on time, accurately identifying allergens, and following recommendations The timely contact with your doctor, accurate identification of cross-allergens and following the recommended preventive measures will help reduce the risk of cross-allergic reactions and improve the quality of life of your patients.
New materials
Popular Articles
We recommend reading
Contact us in the Contact Us section to ask questions, offer ideas, or for more information about our allergy resource.
Our articles are your trusted source of allergy knowledge. Learn how to make life with allergic reactions easier on our specialized portal.
©
Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
© Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
The information on this site is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. We recommend consulting with qualified medical professionals for accurate information and advice.
 English
English  Українська
Українська  Русский
Русский