How to help a child with atopic dermatitis: helpful tips and advice


Irina Makarova
What is atopic dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin disease that often begins to appear at an early age and belongs to the group of atopic diseases. The main manifestations are dry skin, itching and inflammation.
Atopic dermatitis and its classification
Childhood atopic dermatitis is usually classified according to the age of onset and its course. The infant form usually begins in the first six months of life and may disappear before the age of three. The infant form usually begins between the ages of two and five and may continue into adolescence.
Causes of atopic dermatitis in children
- Atopic dermatitis in children is often related to a genetic predisposition. If parents suffer from atopic diseases, the risk of the child developing dermatitis increases.
- Poor environment, air pollution, contact with various chemicals can provoke the development of atopic dermatitis in a child.
- Allergic dermatitis in children can develop due to reactions to food allergens, house dust, plant pollen and other allergens.
Children with atopic dermatitis often have dry and easily irritable skin, which can contribute to the development of the disease.
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis in children
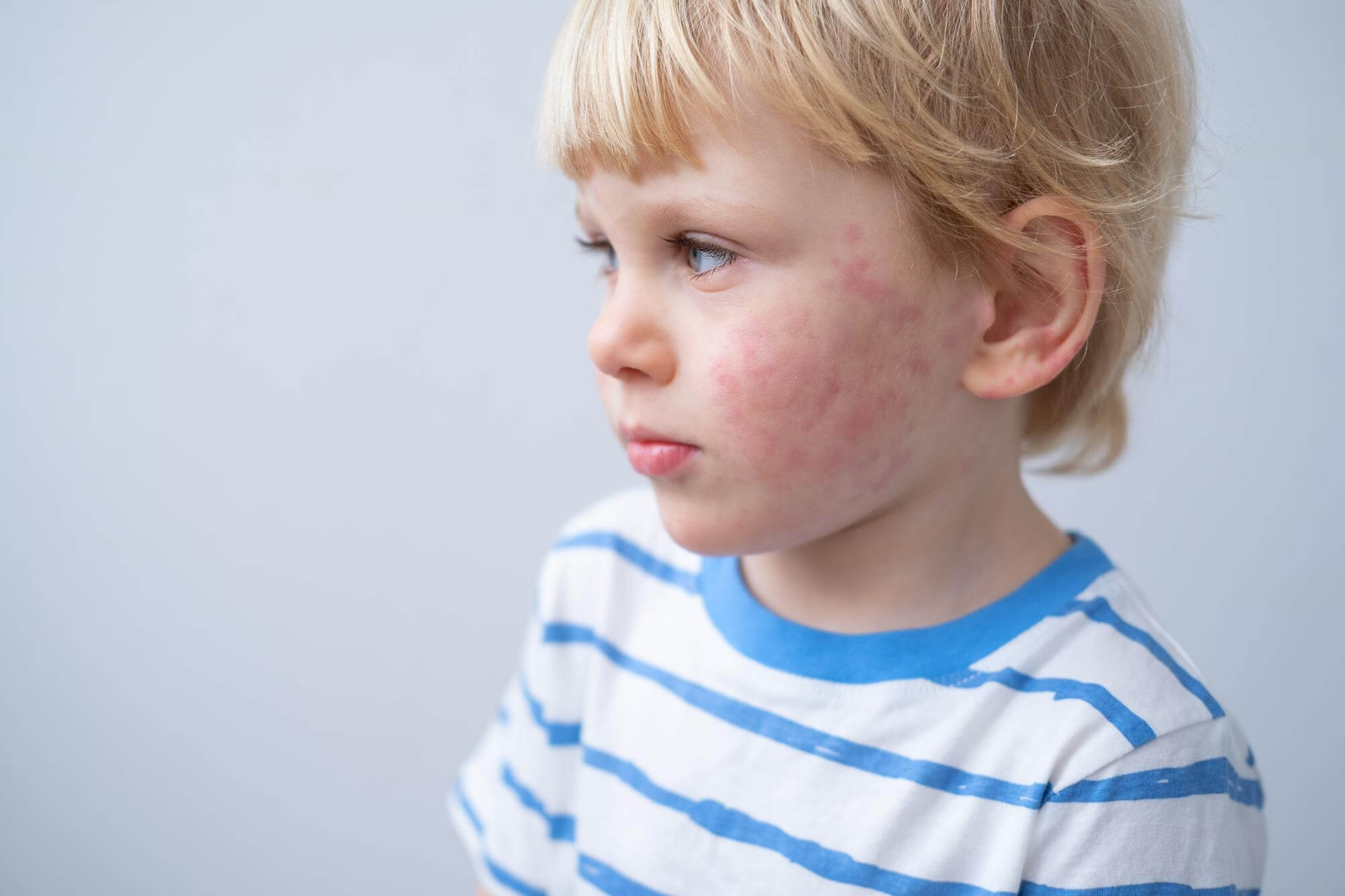
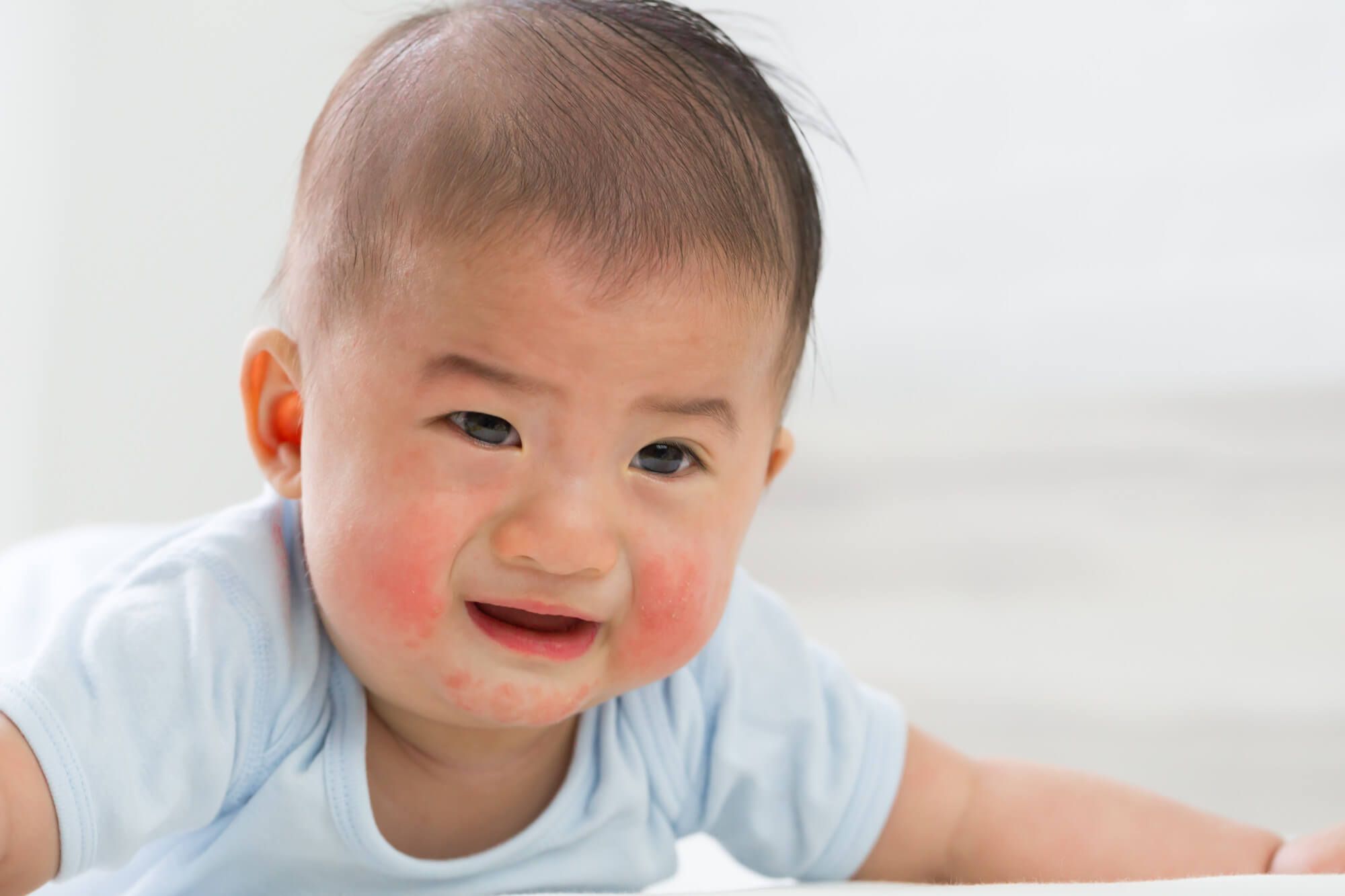
- In newborns, atopic dermatitis usually manifests as redness and dryness of the skin, especially on the cheeks and in the diaper area. There may also be signs of itching, such as anxiety and poor sleep in the infant.
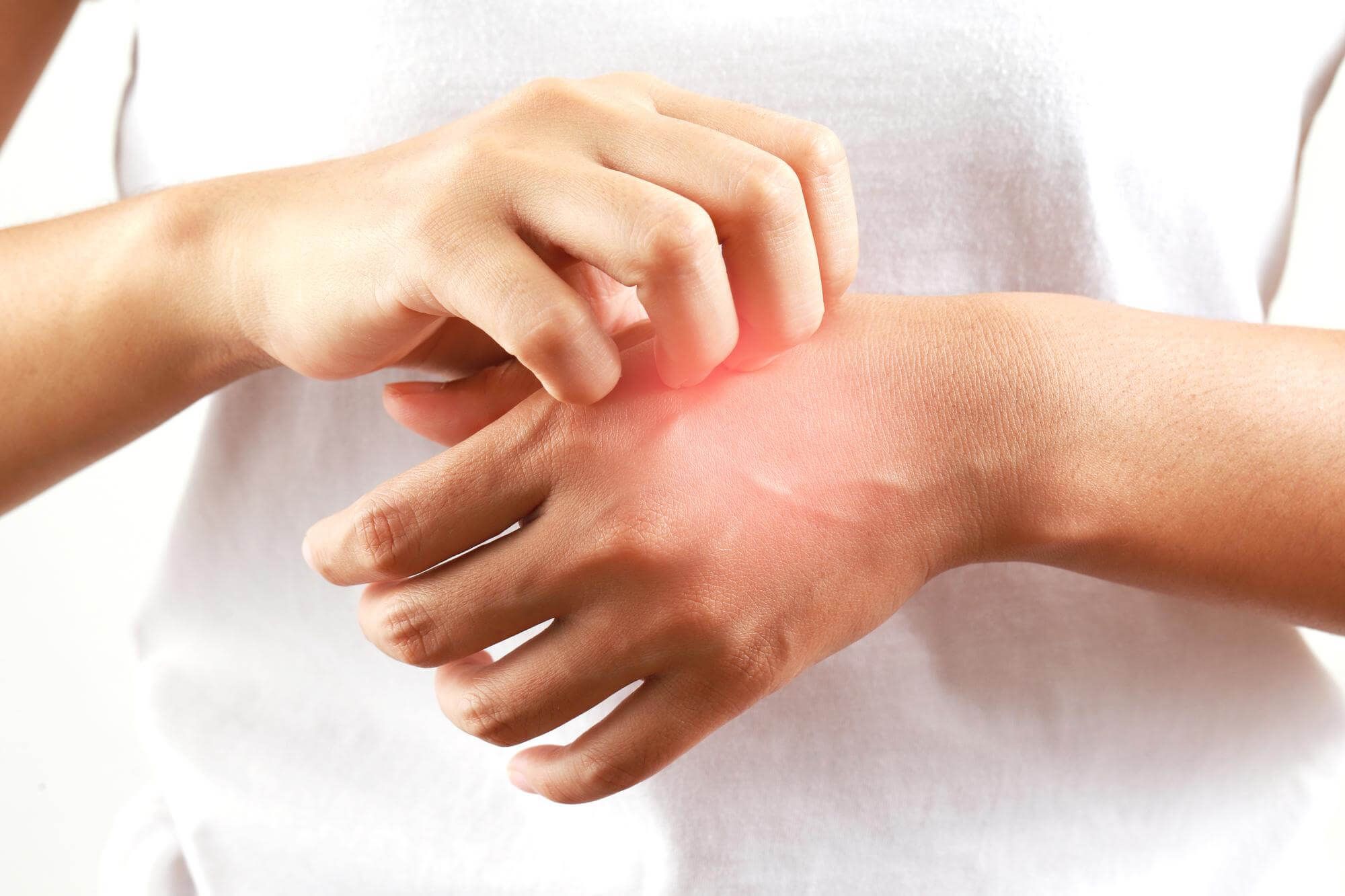
- Atopic dermatitis in children 1 to 3 years old. At this age, symptoms may become more pronounced, with spread to the elbow and knee folds. The skin may become coarser and the itching more intense.
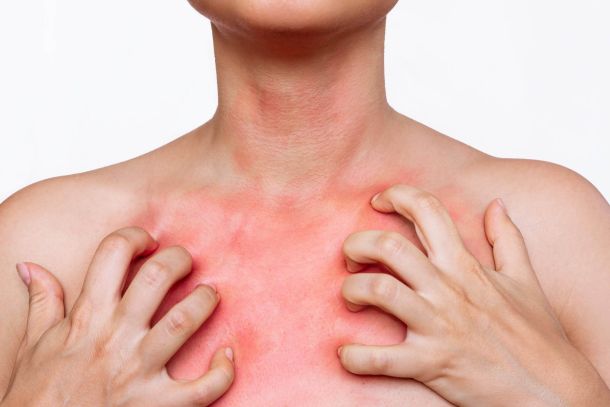
- Atopic dermatitis in children over 3 years of age. In older children, symptoms may focus on the hands, feet, eyelids, and head. Inflammation and itching may worsen during times of stress or illness.
Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis
Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis usually begins with an interview and skin examination. The doctor may also take blood tests for allergies or other tests to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis in children
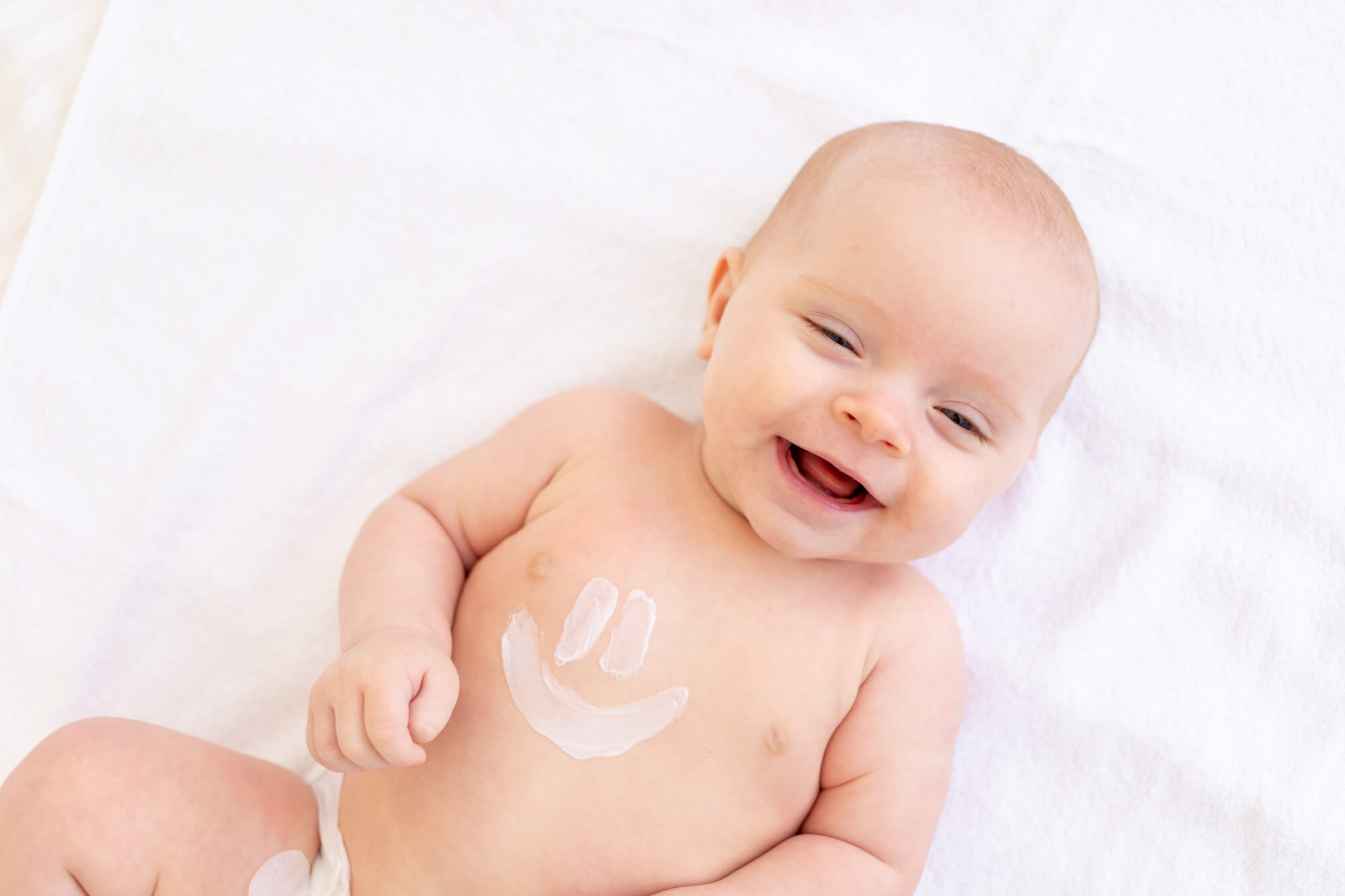

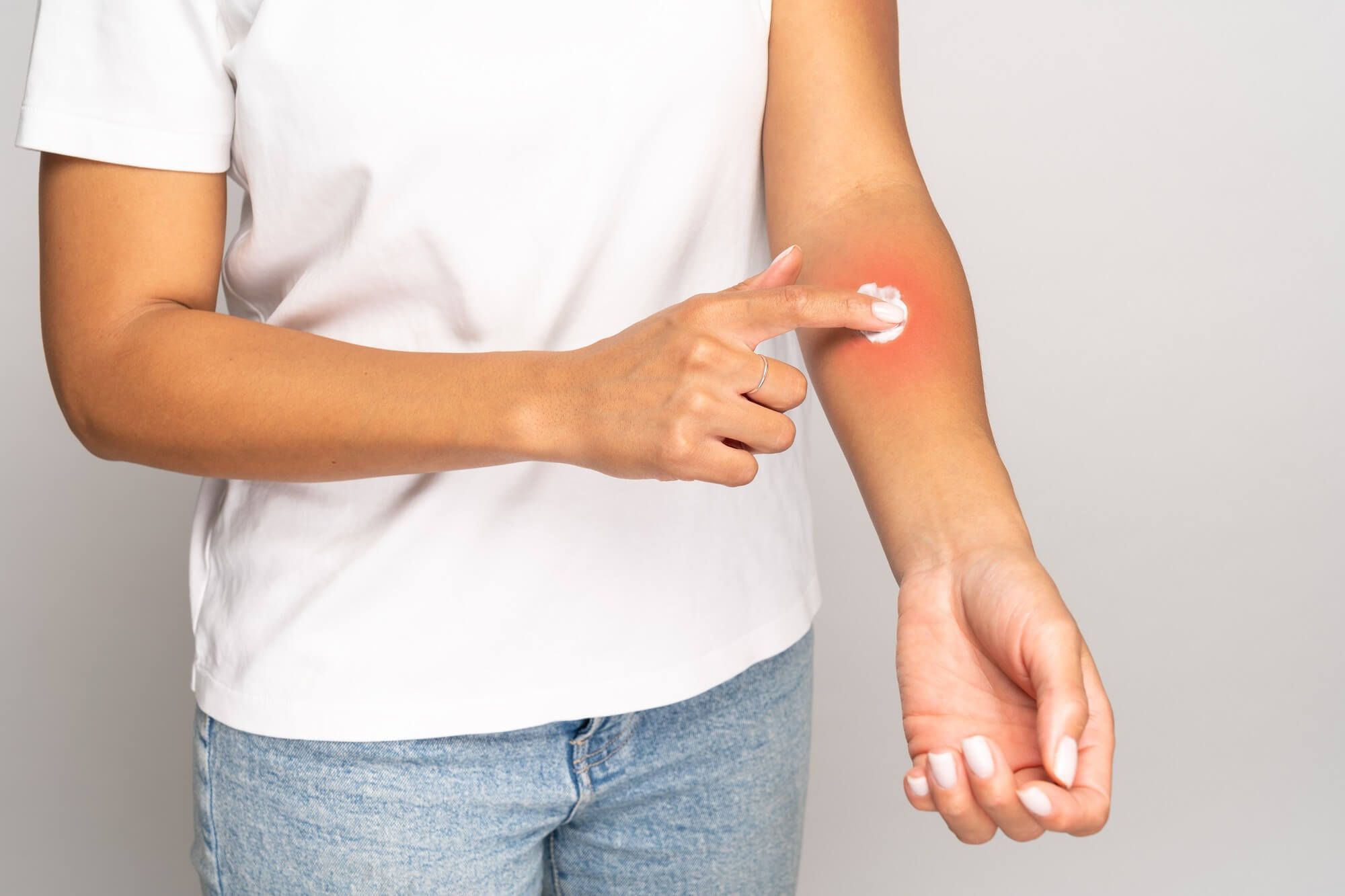
Treatment of atopic dermatitis in children includes the use of medications to moisturize the skin and control inflammation and itching. Corticosteroid ointments, such as Hydrocortisone, or nonsteroidal medications, such as Elocom or Protopik, may be used. In some cases, antihistamines may be needed to control the itching.
In addition to medication, it is important to follow a skin hydration regimen, avoiding known allergens and stressful situations. A consultation with a psychologist may also be helpful for learning how to manage stress and itching.
Prevention of atopic dermatitis
Preventing atopic dermatitis in children includes avoiding contact with known allergens, keeping skin moist and healthy, and seeing an allergist regularly. Proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle also play an important role in preventing the development of this condition.
In conclusion, atopic dermatitis in children is a serious condition that requires a careful approach to treatment and prevention. If your child is showing signs of dermatitis, be sure to see a doctor. Remember that early treatment helps reduce the risk of developing a chronic form of the disease and improves your child's quality of life.
Related Materials
- Treatment of contact dermatitis in children: effective methods
- Effective treatment for allergic dermatitis: the secrets of success
- How to find the perfect ointment to treat allergic dermatitis
- Current approaches to treating and preventing atopic dermatitis
- How to distinguish between sweats and allergies: symptoms and treatment
New materials
Popular Articles
We recommend reading
Contact us in the Contact Us section to ask questions, offer ideas, or for more information about our allergy resource.
Our articles are your trusted source of allergy knowledge. Learn how to make life with allergic reactions easier on our specialized portal.
©
Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
© Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
The information on this site is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. We recommend consulting with qualified medical professionals for accurate information and advice.
 English
English  Українська
Українська  Русский
Русский