Milk allergy guide: symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment


Eva Zakharova
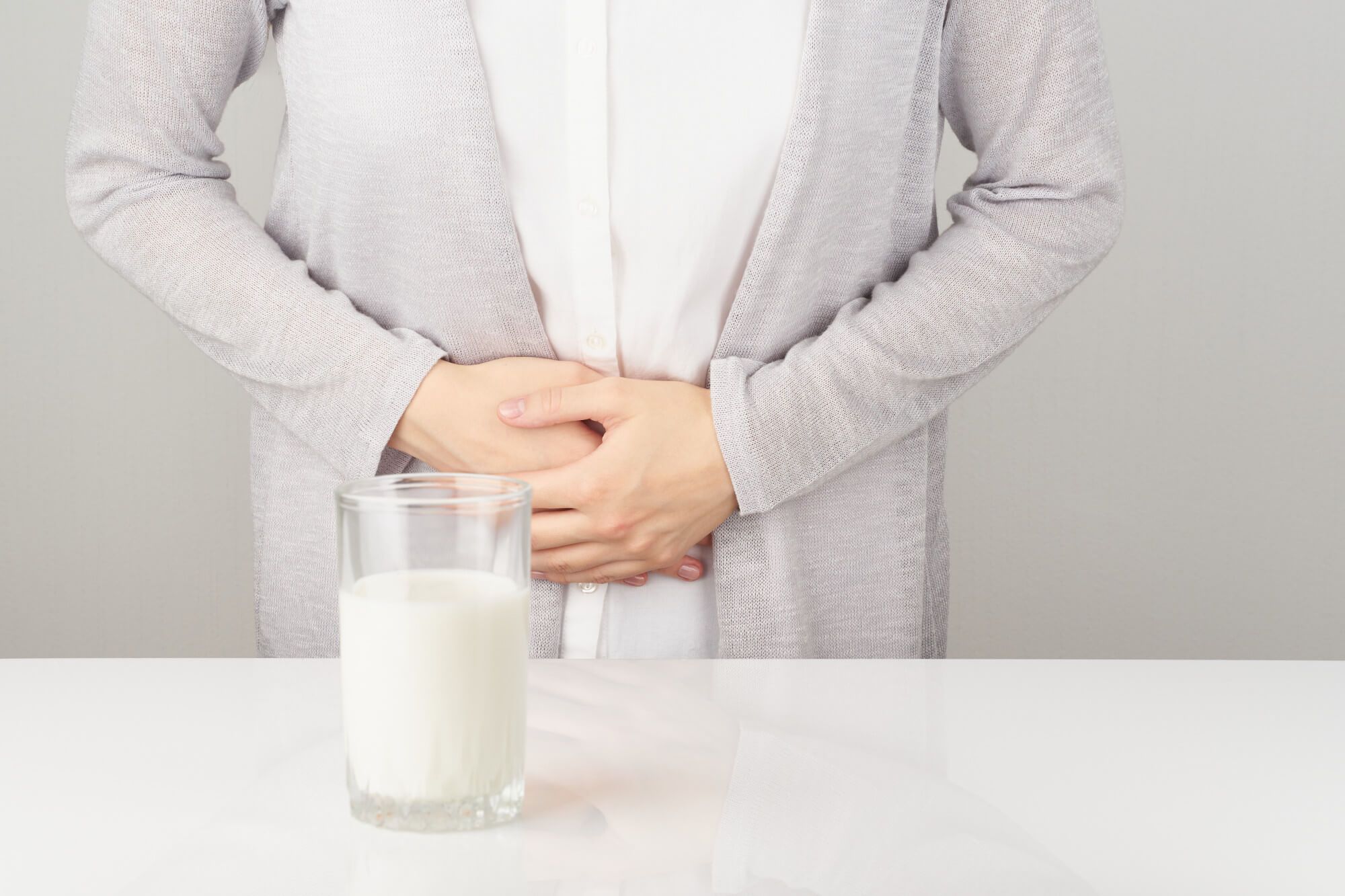
Milk allergy is an immune response of the body to one or more proteins contained in cow's milk. Allergy symptoms can range from mild skin manifestations to severe respiratory symptoms and even anaphylactic shock.
Milk allergy differs from lactose intolerance. In the case of allergy, the immune system reacts to milk proteins, while lactose intolerance is related to the intolerance of the sugar lactose contained in dairy products.
Causes of milk allergy
Milk allergy is associated with immune reactions to milk proteins, such as casein and whey protein. The body perceives these proteins as harmful substances and begins to produce antibodies, which leads to an allergic reaction.
Genetic predisposition
Genetic predisposition also plays a role in the development of milk allergy. If one or both parents suffer from allergies, the likelihood of developing an allergy in the child increases.
Age-related features
Milk allergy is most common in children, especially infants. Most children outgrow this allergy as they age, but in some adults, milk allergy can persist throughout their lives.
Symptoms of milk allergy
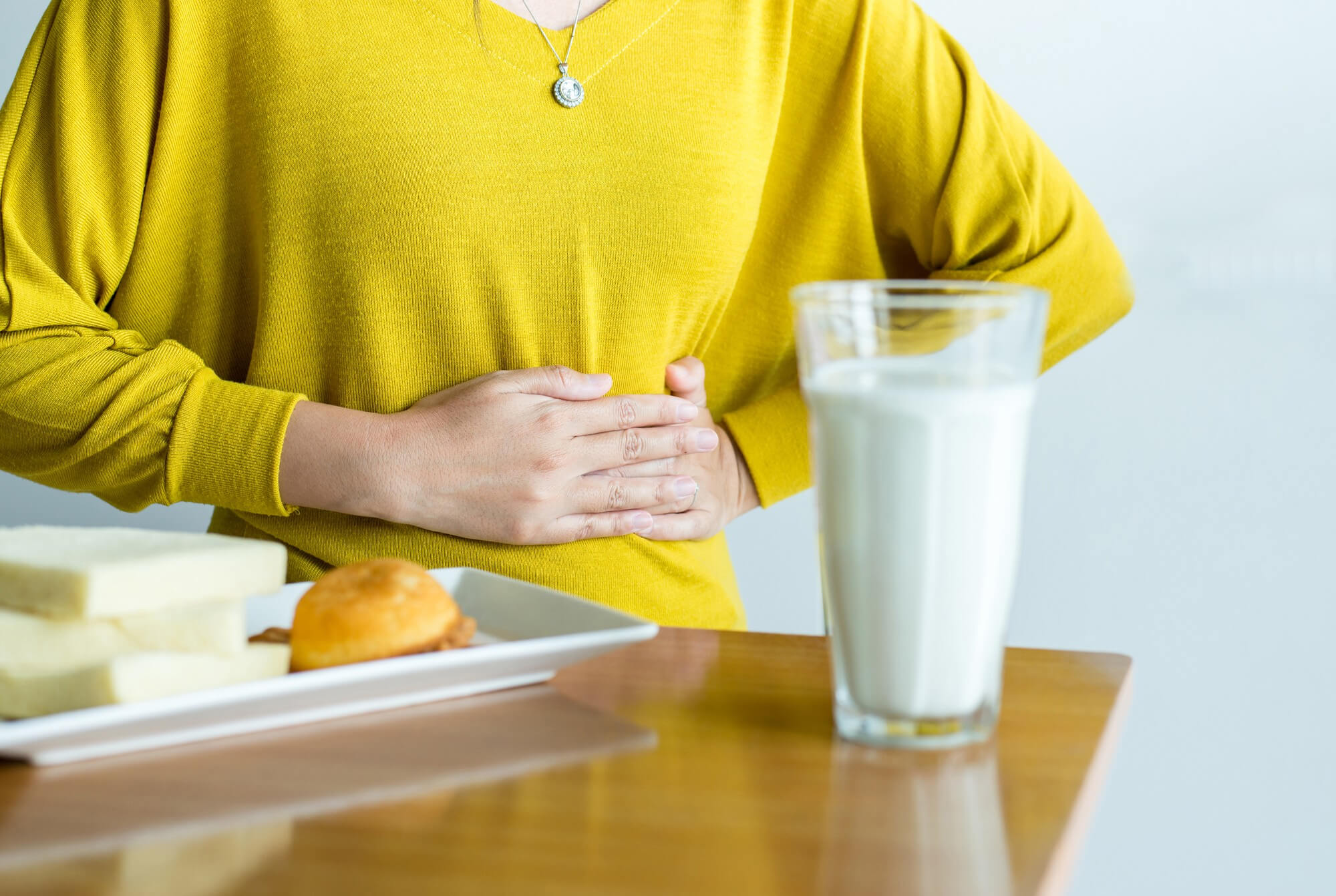

- Skin symptoms of milk allergy include redness, itching, rash, and swelling. In some cases, atopic dermatitis may develop.
- Digestive symptoms of milk allergy include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. In newborns, milk allergy can cause colic and constipation.
- Respiratory symptoms of milk allergy may include a runny nose, itching and tearing of the eyes, cough, difficulty breathing, and wheezing.
Milk allergy diagnosis
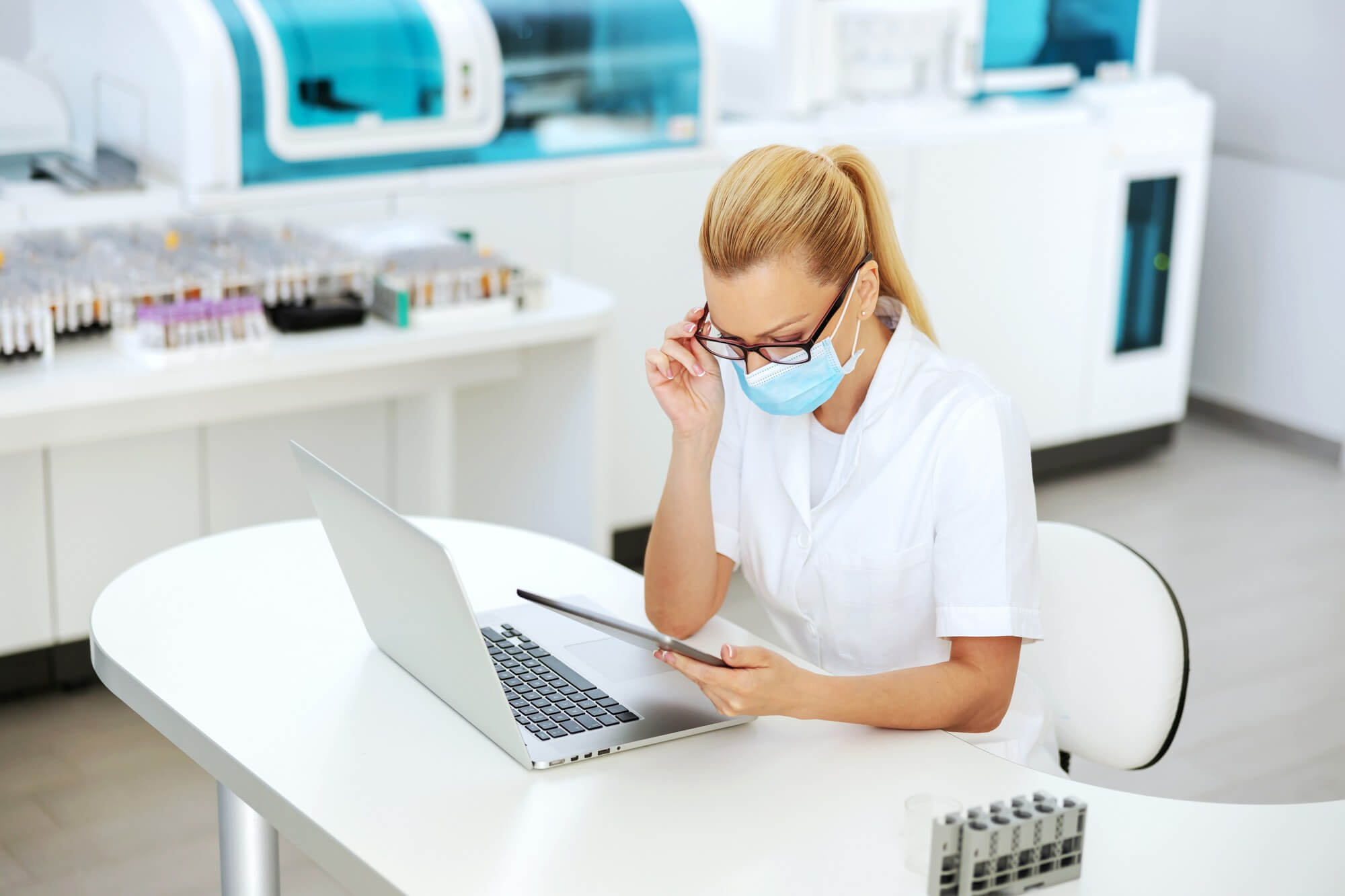

For the diagnosis of milk allergy, an allergist will first conduct a medical history and clinical examination. It is important to inform the doctor about all symptoms and their connection with the consumption of dairy products.
Blood test for Immunoglobulin E (IgE)
- A blood test for Immunoglobulin E (IgE) helps to determine the presence of antibodies indicating a milk allergy. An elevated level of IgE may indicate an allergic reaction.
Skin tests
- Skin tests are also used for the diagnosis of milk allergy. The doctor applies a small amount of milk protein extract to the skin and observes the reaction. If redness or swelling occurs, this may indicate an allergy.
Elimination diet and provocation tests
- In some cases, a doctor may recommend an elimination diet, in which dairy products are completely excluded from the diet for a certain period of time. If symptoms decrease and then return after reintroducing dairy products, this may confirm a milk allergy diagnosis.
Milk allergy treatment
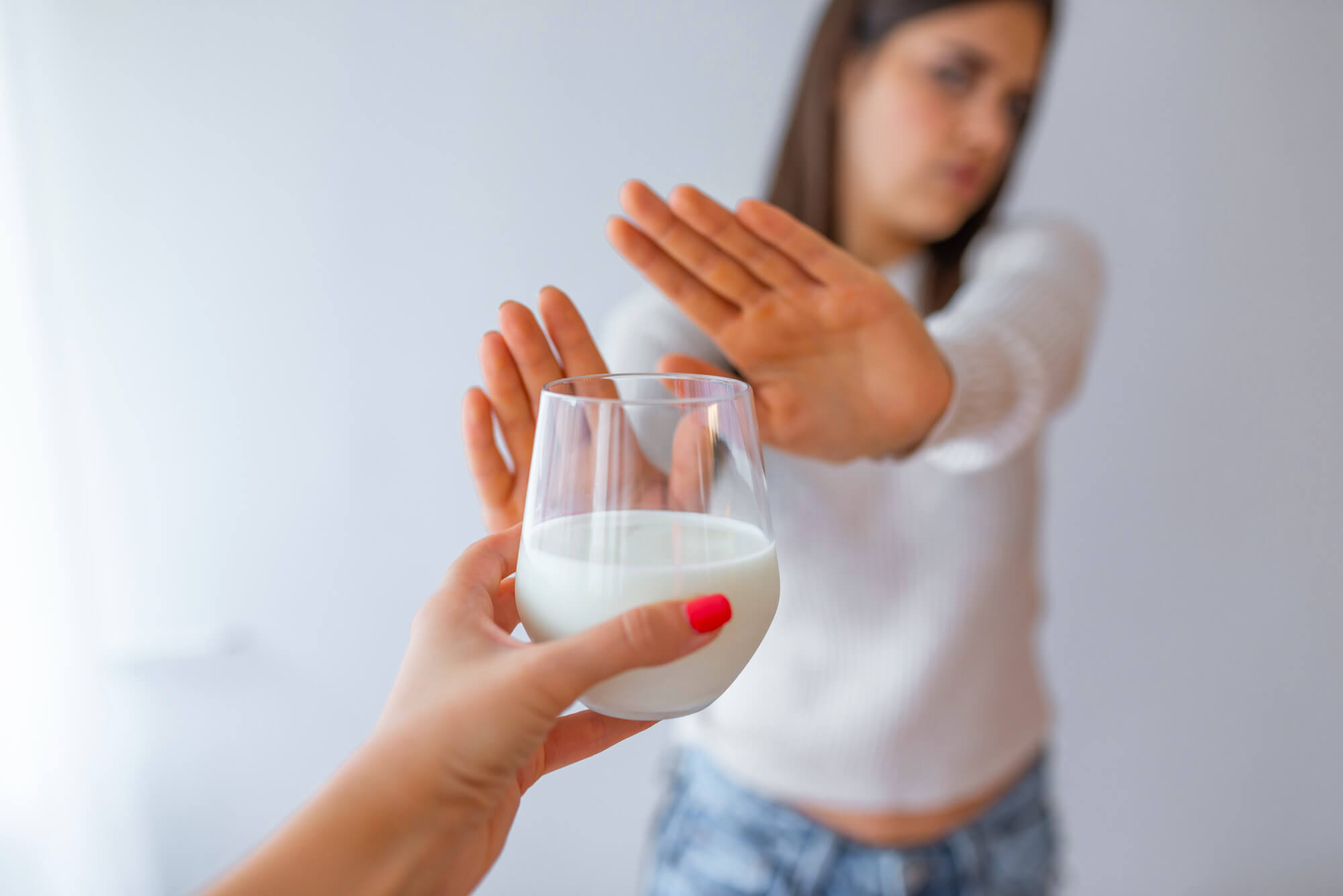

The main method of treating milk allergy is to exclude dairy products from the diet. It's important to know what not to eat and to carefully study the composition of products when shopping.
Antihistamine medications (Cetirizine, Loratadine, Fexofenadine, Desloratadine, Ebastine) can be used to relieve allergy symptoms such as itching, rash, and swelling. They should be taken as prescribed by a doctor.
Depending on the symptoms of milk allergy, a doctor may also recommend symptomatic treatment, such as medications for easier breathing or remedies for diarrhea.
Dairy alternatives
There are many plant-based milk substitutes, such as soy, almond, and oat milk. They can be used instead of cow's milk for preparing various dishes and beverages.
Dairy-free diet: tips and recommendations
When following a dairy-free diet, it is important to ensure a balanced intake of all necessary macro- and micronutrients. Plant-based milks and other dairy substitutes can help with this. Also, pay attention to the composition of products, as milk protein may be present in various products, including bread, sausage, and ready-made sauces.
Which products can cause cross-reactivity with milk?
Cross-reactivity occurs when the immune system reacts to similar proteins from different products. In the case of milk allergy, cross-reactions may occur with goat and sheep milk, as well as with products containing animal protein, such as beef and veal.
Milk allergy in children
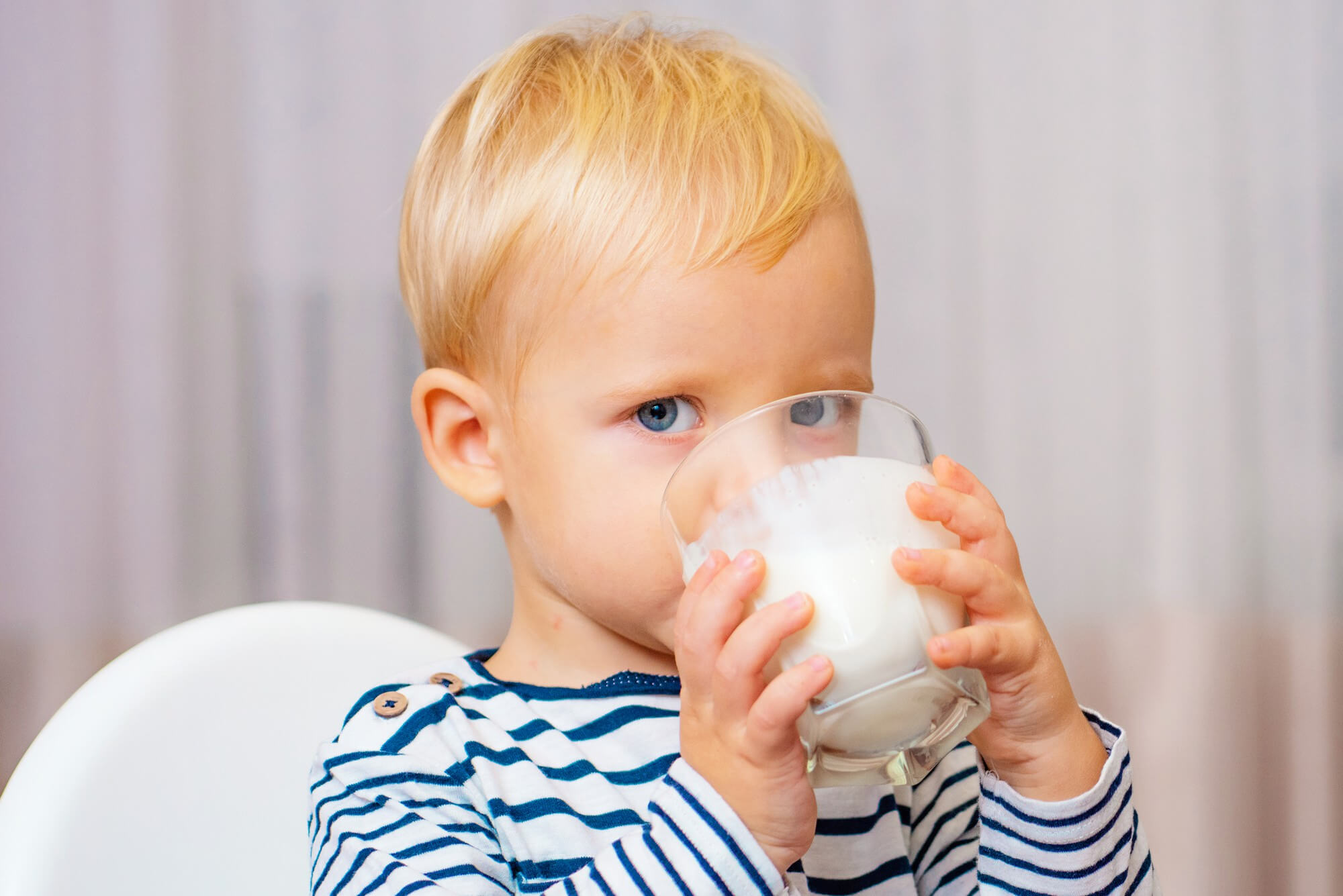

Milk allergy in infants can manifest with various symptoms, including skin reactions, digestive disorders, and respiratory symptoms. In some children, milk allergy may resolve with age, but the decision to introduce dairy products into the diet should only be made after consulting a doctor.
Introducing dairy products during breastfeeding
During breastfeeding, dairy products can be gradually introduced into the mother's diet and the baby's reaction can be observed. If symptoms of milk allergy occur, dairy products should be excluded from the mother's diet and a doctor should be consulted.
Milk allergy and adapted formulas
Adapted formulas can be used as a substitute for breast milk for children with milk allergy. It is important to choose formulas without cow's milk and pay attention to the composition of the product. The decision on choosing a formula should be made jointly with a pediatrician or allergist.
In conclusion, milk allergy is a common occurrence, especially among children. Allergy symptoms can range from skin manifestations to digestive and respiratory symptoms. It is important to consult a doctor for accurate diagnosis and treatment. The main treatment method is the exclusion of dairy products from the diet, as well as the use of antihistamines and symptomatic treatment if necessary. There are many alternatives to dairy products that can help maintain a balanced diet without using cow's milk. Be attentive to the composition of products and be aware of possible cross-reactions with other products containing animal protein.
New materials
Popular Articles
We recommend reading
Contact us in the Contact Us section to ask questions, offer ideas, or for more information about our allergy resource.
Our articles are your trusted source of allergy knowledge. Learn how to make life with allergic reactions easier on our specialized portal.
©
Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
© Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
The information on this site is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. We recommend consulting with qualified medical professionals for accurate information and advice.
 English
English  Українська
Українська  Русский
Русский