Potato allergy: how to live and eat without risk to health?


Eva Zakharova
Potato allergy is a rare type of food allergy, although it can be a serious problem for some people. It has been noted that a child's potato allergy can manifest itself more vividly than an adult's. In this article, an experienced allergist will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment of this condition, as well as whether potato starch and raw potatoes can cross-allergy.
Causes of potato allergy
The main cause of allergy to potatoes is the presence of specific proteins in it, which cause an immune reaction of the body. Among them are patatin, protease inhibitors and lectin. People vulnerable to allergies have a genetic predisposition to develop this disease.
Potato allergy symptoms
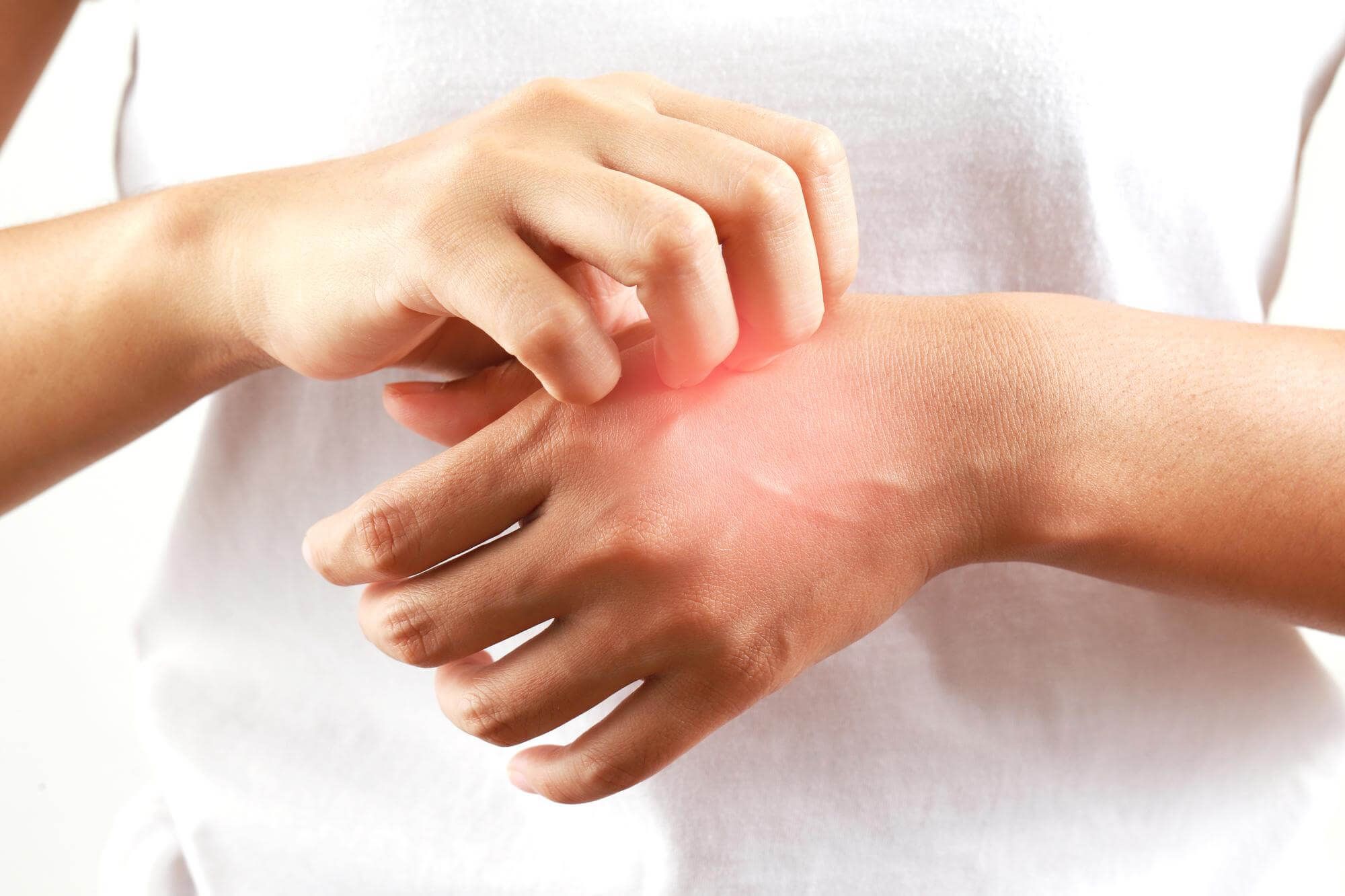
Symptoms of potato allergy can range from mild to severe. They include itching and redness of the skin, rashes, swelling, runny nose, difficulty breathing, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. In rare cases, anaphylactic shock may occur.
Potato allergy types

Rain potatoes
Some people are allergic only to raw potatoes, because the heat treatment destroys some of the allergens. It is important to remember that raw potatoes can also cause cross-allergies with other foods that contain similar proteins, such as tomatoes or eggplant.
Cooked potatoes
In some cases allergies can be triggered by cooked potatoes, where the allergens remain active even after they have been heated. In a child an allergy to cooked potatoes may appear in the form of hives or swelling, as well as gastrointestinal problems.
Potato starch
Allergies to potato starch are less common, but can be especially dangerous because starch is found in many foods and supplements. Such allergies can cause digestive problems, skin manifestations and even anaphylactic shock.
Diagnosis of potato allergy
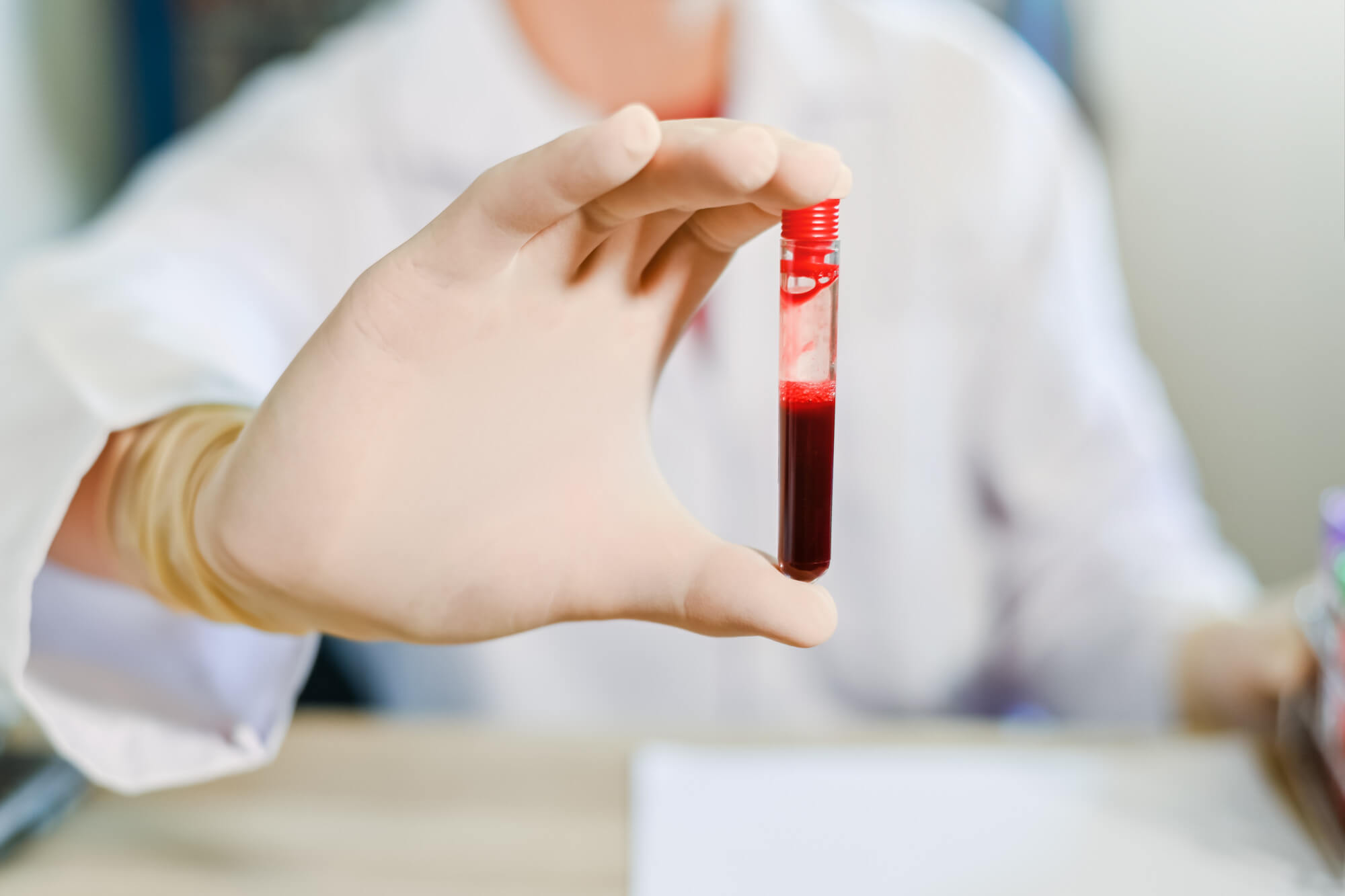

- A blood test for immunoglobulin E (IgE) can detect the presence of antibodies to potato allergens and confirm the diagnosis of potato allergy.
- Skin tests are performed by applying the potato extract to the skin and observing the reaction. If the result is positive, redness and itching appear at the site of contact with the allergen.
- An elimination diet involves temporarily excluding potatoes from the patient's diet, followed by their gradual introduction back into the menu. If the allergy symptoms disappear when the potatoes are excluded and return when they are introduced, this confirms the diagnosis of potato allergy.
Treatment of potato allergy
To treat potato allergy, the doctor may prescribe antihistamines such as Cetirizine, Loratadine, or Fexofenadine, and corticosteroid ointments such as Hydrocortisone or Betamethasone to relieve the skin manifestations of the allergy.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy for potato allergy involves the administration of small doses of the allergen, to gradually get the body used to and reduce sensitivity to potato allergens. This method of treatment must be supervised by an experienced allergist and may take a long time.
People's medicine remedies
Although folk remedies cannot completely cure potato allergy, they can help relieve some of the symptoms. Decoctions and infusions of herbs, such as nettle, St. John's wort, or motherwort, for example, can reduce itching and inflammation of the skin. However, you should consult a doctor before using folk remedies.
Preventing potato allergies

- To reduce the risk of allergies to potatoes, it is important to store them in a dark, cool and dry place to prevent mold formation and an increase in solanine, which can aggravate an allergic reaction.
- If you or your child is allergic to potatoes, you should eliminate them from your diet completely. Pay attention to the composition of foods, as potato starch can be found in many of them. Variety your menu by including other sources of carbohydrates and fiber.
- Foods such as buckwheat, corn, rice, or yacon potatoes can be used for potato allergies that do not cause an allergic reaction and can be a substitute for potatoes in your diet.
Potato allergy is a rare but serious condition that requires attention and proper treatment. It is important to be aware of the possible symptoms and causes of potato allergies, especially in a child, and to use effective methods of diagnosis and treatment. If you suspect a potato allergy, be sure to see an allergist for a comprehensive examination and prescribe a suitable treatment. Taking preventative measures, such as storing potatoes properly and paying attention to the composition of the food, can help reduce the risk of allergies and make your life and your child's life easier.
Related Materials
- Fighting strawberry allergy: causes, symptoms, and modern treatment methods
- Allergy to cottage cheese: how to recognize and treat it?
- Honey Allergy: Causes, symptoms, and treatment Methods
- Watermelon allergy: symptoms and treatment methods
- The complete guide to shrimp allergies: from symptoms to treatment
New materials
Popular Articles
We recommend reading
Contact us in the Contact Us section to ask questions, offer ideas, or for more information about our allergy resource.
Our articles are your trusted source of allergy knowledge. Learn how to make life with allergic reactions easier on our specialized portal.
©
Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
© Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
The information on this site is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. We recommend consulting with qualified medical professionals for accurate information and advice.
 English
English  Українська
Українська  Русский
Русский