What you need to know about cold allergy: symptoms and treatment


Eva Zakharova
Cold allergy, also known as cold urticaria or cold allergy syndrome, is an allergic reaction of the body to low temperatures, cold air, wind, or contact with snow. This common condition can affect people of all ages, including children.
Definition of cold allergy
Cold allergy occurs when the immune system reacts to cold as a harmful substance, leading to an allergic reaction. This condition is characterized by skin symptoms such as itching, redness, swelling, and hives similar to urticaria (cold urticaria). Respiratory and cardiovascular symptoms may also occur.
Causes of cold allergy
The causes of cold allergy can vary. In some cases, it is a hereditary condition that is passed down genetically. In other cases, it may be caused by other allergies or illnesses. Psychosomatic factors may also play a role in the development of cold allergy. Additionally, people with weakened immune systems are more likely to develop cold allergy.
Risk of developing cold allergy
The risk of developing cold allergy increases in individuals with a hereditary predisposition, patients with other allergic diseases, as well as in people with weakened immune systems.
Symptoms of cold allergy
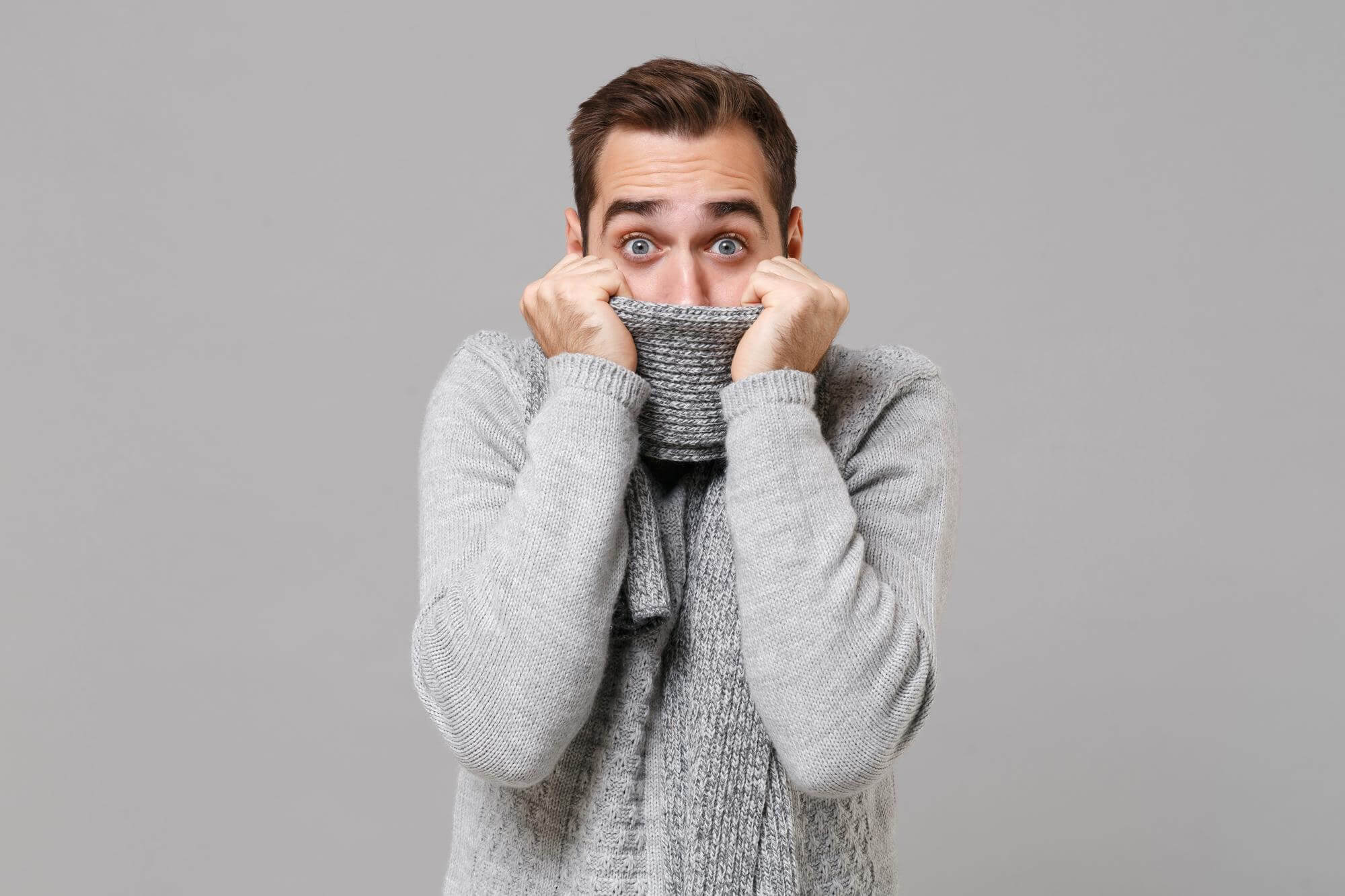

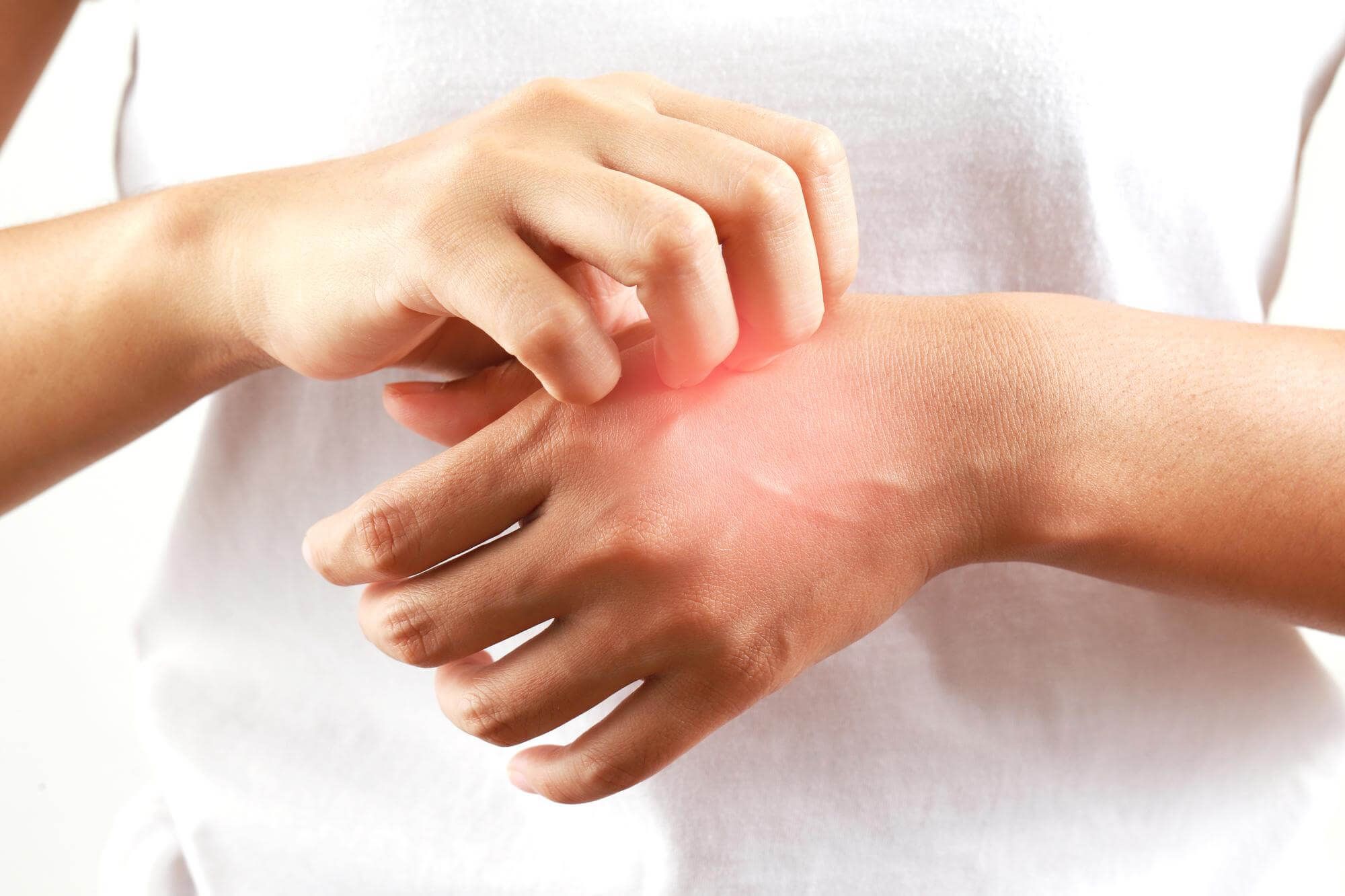
- Skin manifestations of cold allergy include itching, redness, swelling, and hives similar to urticaria (cold urticaria). The rash can appear on the hands, feet, face, or other parts of the body that are exposed to cold. In some cases, the skin may become painful and sensitive to the touch.
- Cold allergy can also cause respiratory symptoms such as difficulty breathing, coughing, runny nose, or asthma attacks, especially when inhaling cold air.
- In some people, cold allergy can cause cardiovascular symptoms such as dizziness, fainting, rapid heartbeat, or even angina.
Diagnosis of cold allergy
To diagnose cold allergy, a cold stimulation test can be used. During this test, the patient's skin is exposed to contact with a cold object (such as an ice cube) for several minutes. If a rash, swelling, or redness appears on the skin after this, it indicates the presence of cold allergy.
An allergist may also order additional tests such as blood tests or skin tests for other allergens to rule out or confirm the presence of cold allergy and determine appropriate treatment.
Treatment of cold allergy

Medication treatment
Treatment of cold allergy includes the use of antihistamines (cetirizine, loratadine, fexofenadine), such as tablets or syrups, which help to reduce itching, redness, and swelling.
In some cases, the doctor may prescribe hormonal creams (hydrocortisone ointment) containing corticosteroids for local application to affected areas of the skin. These creams help reduce inflammation and itching associated with cold allergy.
Non-Drug Treatment
One of the main methods for treating and preventing cold allergy is to avoid contact with the cold. This includes wearing warm clothing, using gloves, hats, and scarves when going outside in winter, as well as limiting the time spent in the cold.
Moisturizing the Skin
Keeping the skin moisturized can help prevent dryness and itching caused by cold allergy. Regular use of moisturizing creams and body oils promotes skin health and reduces the likelihood of allergic reactions to the cold.
Prevention of cold allergy

To prevent the development of cold allergy, it is important to choose clothing appropriate to the weather conditions. Use warm layers of clothing, breathable materials to retain heat and prevent hypothermia.
Strengthening the immune system
Taking care of your health and immunity also plays an important role in preventing cold allergies. Maintain a healthy lifestyle, eat a varied and vitamin-rich diet, engage in sports and ensure adequate sleep.
Protection of the skin from the cold
Use protective skin care products such as moisturizing creams and oils, special lip balms, and sun protection when going out in the cold. This will help prevent dryness, loss of moisture, and skin irritation.
Vitamins and minerals for allergy prevention
Proper nutrition, rich in vitamins and minerals, also helps strengthen the immune system and can help prevent cold allergies. Vitamins B, C, D, as well as zinc and magnesium are especially important.
Cold allergies in children

Cold allergies can manifest particularly strongly in children because their skin is more sensitive to external influences. In addition, children's immune systems are not yet fully formed, which can contribute to the development of allergic reactions.
Treatment and prevention in infants
The treatment of cold allergy in children includes both medication and non-medication approaches similar to adults. However, before using any medication, it is important to consult with a doctor, as some drugs may be contraindicated for children or require different dosages than those for adults. Prevention of cold allergy in children also involves proper clothing, strengthening the immune system, and protecting the skin from the cold.
Cold allergy is a fairly common condition that can manifest itself in various symptoms and lead to serious complications. To successfully treat and prevent this disease, it is important to timely consult an allergist, strictly follow their recommendations, and take care of one's health and immunity.
New materials
Popular Articles
We recommend reading
Contact us in the Contact Us section to ask questions, offer ideas, or for more information about our allergy resource.
Our articles are your trusted source of allergy knowledge. Learn how to make life with allergic reactions easier on our specialized portal.
©
Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
© Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
The information on this site is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. We recommend consulting with qualified medical professionals for accurate information and advice.
 English
English  Українська
Українська  Русский
Русский