Allergic arthritis: symptoms, causes, and treatment

Viktor Levchenko
Allergic arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joints caused by the body's allergic reaction to various external and internal factors. In this article, an experienced allergist will review the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of allergic arthritis, as well as tips for preventing the disease.
Definition of allergic arthritis
Allergic arthritis is a rare joint disease that is caused by allergic reactions to various substances or infectious agents. Infectious allergic arthritis results from exposure to an infectious agent that causes an allergic reaction and inflammation of the joints.
Causes of allergic arthritis
Causes of allergic arthritis can be varied, including:
- Direct exposure of the joints to an allergen (food allergens, medications, plant pollen, etc.);
- Infectious agents such as bacteria, viruses or fungi that cause allergic arthritis through the immune system;
- Autoimmune processes, when the immune system attacks the joints' own tissues, mistaking them for foreign substances.
Symptoms of allergic arthritis

С Symptoms of allergic arthritis can vary and vary depending on age, the severity of the disease, and individual body characteristics. Common signs of allergic arthritis include:
- Inflammation and swelling of the joints;
- Pain in the joints that increases with movement;
- Redness and increase in temperature of the skin over the joint;
- Morning stiffness and limitation of movement;
- General weakness, elevated body temperature, and fatigue.
Allergic arthritis symptoms in children
Allergic arthritis in children may present with the following symptoms:
- Pain and swelling of the joints, especially the knees, elbows, and wrists;
- A tendency to frequent respiratory illnesses;
- Allergic skin reactions, such as urticaria or atopic dermatitis;
- Lameness, especially after sitting or sleeping for long periods of time;
- Irritability and increased fatigue.
Symptoms of allergic arthritis in adults
In adults, allergic arthritis may manifest as follows:
- Inflammation and pain in one or more joints;
- Morning stiffness and limitation of movement in the joints, which can last up to several hours;
- Various allergic manifestations, such as hives, Quincke's edema, or asthma;
- Sometimes internal organs such as the kidneys, liver, or heart may be affected.
Diagnosis of allergic arthritis

During the visit, the specialist will take a medical history and perform a physical examination of the patient, assessing the condition of the joints, skin and internal organs. The doctor will also clarify the presence of a Allergic reactions, family history, and the presence of chronic diseases.
To confirm the diagnosis of allergic arthritis, the following laboratory tests may be prescribed:
- General blood tests, which may reveal elevated white blood cell count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and C-reactive protein;
- Immunological tests, including determination of immunoglobulin levels (IgE, IgA, IgM, IgG) and antibodies to allergens;
- Allergy tests, such as skin tests or allergen blood tests to help identify specific allergens that cause arthritis.
Instrumental diagnostic methods
In some cases, instrumental diagnostic methods may be prescribed, such as:
- X-rays of the joints, which can reveal the extent of joint damage and the presence of degenerative changes;
- Ultrasound of the joints, which can assess the degree of inflammation and the presence of effusion;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for a more detailed study of the structure of the joints and surrounding tissues.
Treatment of allergic arthritis
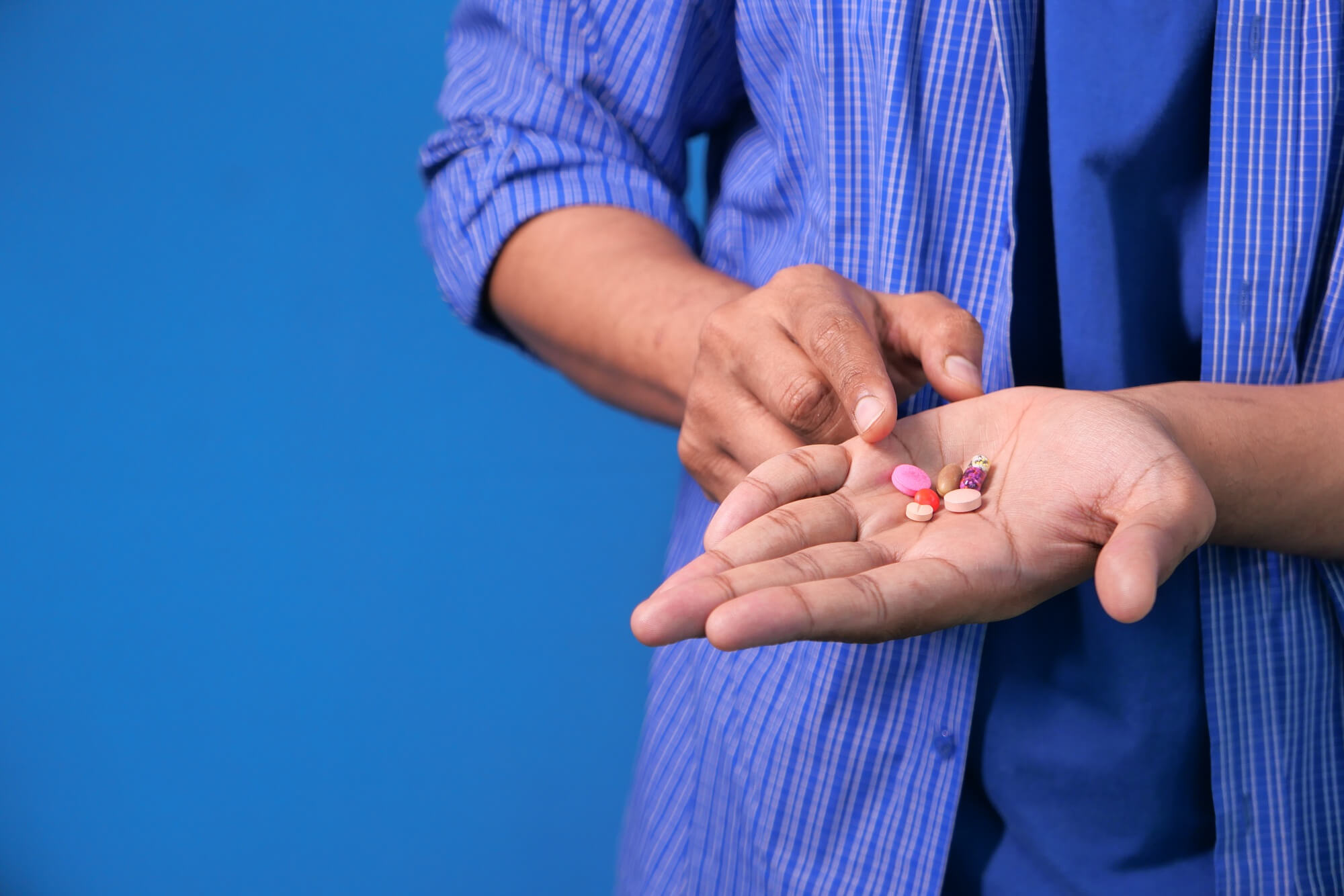
Treatments for allergic arthritis include various groups of medications to address inflammation, pain, and the allergic reaction.
Anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen, diclofenac, or naproxen are used to reduce inflammation and joint pain.
In severe forms of allergic arthritis or the presence of autoimmune processes, immunosuppressants such as methotrexate, cyclos osporine or azathioprine, which suppress the immune system and reduce the activity of the inflammatory process.
Physical therapy and rehabilitation
An important component of allergic arthritis treatment is physical therapy, which helps restore joint function and strengthen the surrounding muscles. Physical therapy methods include massage, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, ultrasound therapy, and mud therapy.
Alternative therapies
Some patients with allergic arthritis may use alternative therapies such as homeopathy, folk remedies, or acupuncture. However, consultation with a physician is necessary before using alternative therapies.
Tips for preventing allergic arthritis
Prevention of allergic arthritis includes the following measures:
- Avoiding contact with known allergens;
- Following a hypoallergenic diet;
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and weight control;
- Preventing and treating infectious diseases;
- Regular visits to the doctor to monitor the condition of the joints and take preventive measures.
In conclusion, allergic arthritis is a disease that requires timely diagnosis and a comprehensive approach to treatment. By seeing a doctor and following his recommendations, most patients with allergic arthritis can achieve significant improvement in their condition and maintain joint function.
Related Materials
New materials
Popular Articles
We recommend reading
Contact us in the Contact Us section to ask questions, offer ideas, or for more information about our allergy resource.
Our articles are your trusted source of allergy knowledge. Learn how to make life with allergic reactions easier on our specialized portal.
©
Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
© Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
The information on this site is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. We recommend consulting with qualified medical professionals for accurate information and advice.
 English
English  Українська
Українська  Русский
Русский