Microbial eczema: causes and symptoms

Irina Makarova
What is microbial eczema?
Microbial eczema is a type of inflammatory skin disease known as eczema. This form is characterized by the appearance of inflammatory elements on the skin that are often caused by certain types of microorganisms.
Causes of microbial eczema
- Various microorganisms are always present on our skin. Under normal conditions, they live in balance and do not cause problems. However, under certain circumstances, such as a weakened immune system or an imbalance of the skin's normal microflora, these microorganisms can cause inflammation, including microbial eczema.
- Risk factors for microbial eczema include a weakened immune system, chronic diseases, long-term use of antibiotics, improper diet, stress, and a predisposition to allergic reactions.
- Improper skin care, insufficient or excessive hygiene can also contribute to the development of microbial eczema. It is important to keep the skin clean, but not to over-dry it, as this can break its protective barrier and contribute to the development of inflammation.
Symptoms of microbial eczema
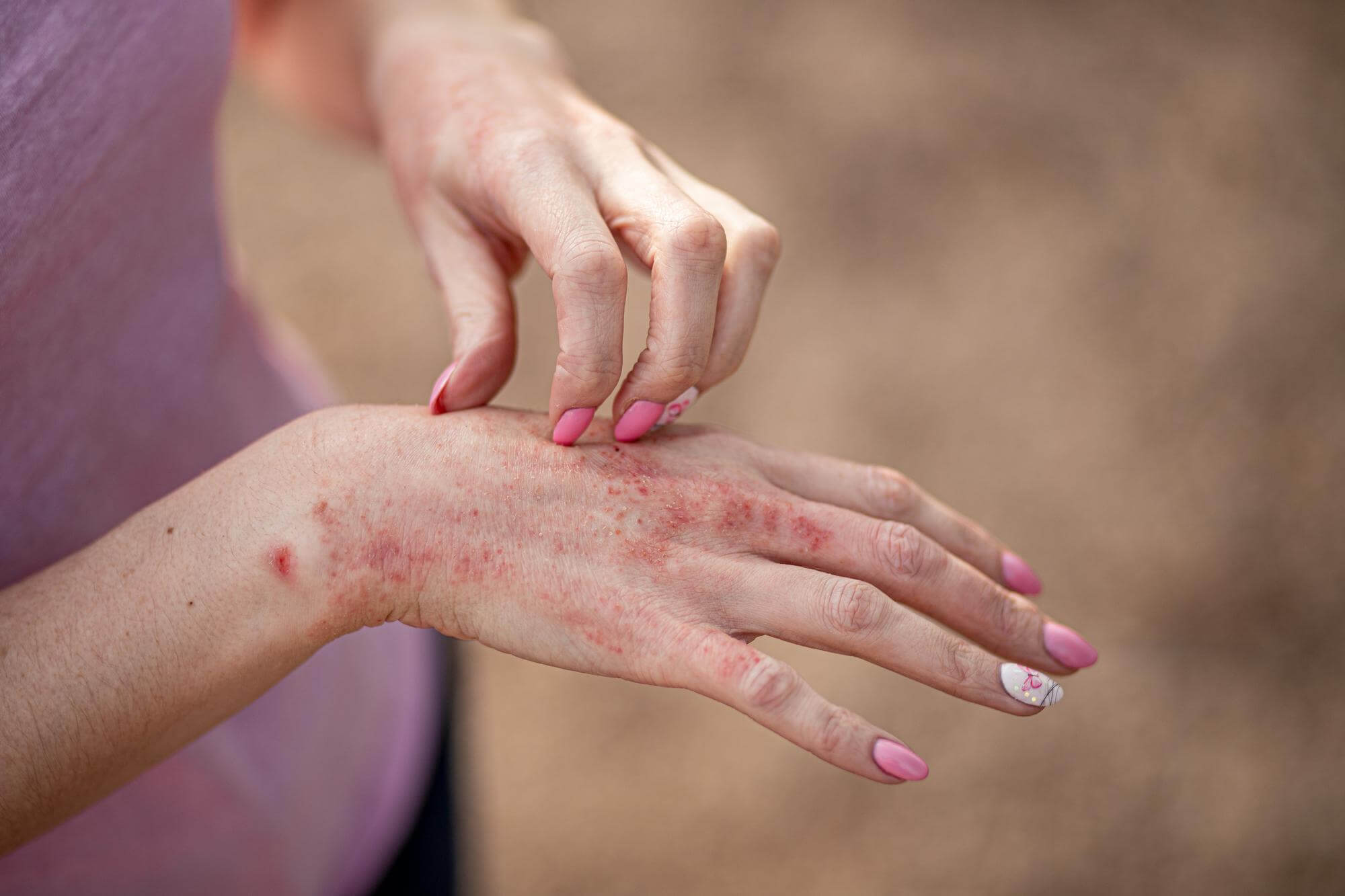

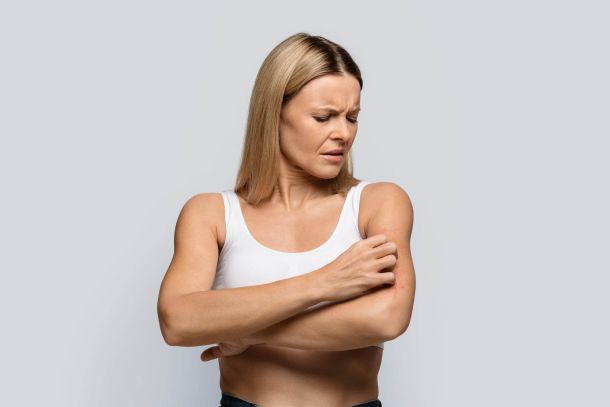
Symptoms of microbial eczema may include: itching, redness, swelling, and formation of inflammatory elements on the skin, including the face, legs, hands, and shins. They may have varying degrees of severity depending on the individual characteristics of the body.
Peculiarities in children and adults
In children and adults, microbial eczema can manifest itself in slightly different ways. In children, it is often more active, with more vivid symptoms, while in adults it is more chronic, with periods of exacerbation and remission.
Differences between microbial and other types of eczema
In contrast to other types of eczema, microbial eczema is often associated with an imbalance of the skin's microflora and the activation of certain microorganisms. This makes its treatment somewhat different from other types of eczema.
Diagnosis of microbial eczema
Diagnosis of microbial eczema includes a visual examination, history, and microbiological analysis to identify the microorganisms that cause the inflammation. In some cases, additional testing may be necessary to rule out other skin conditions.
Treatment of microbial eczema
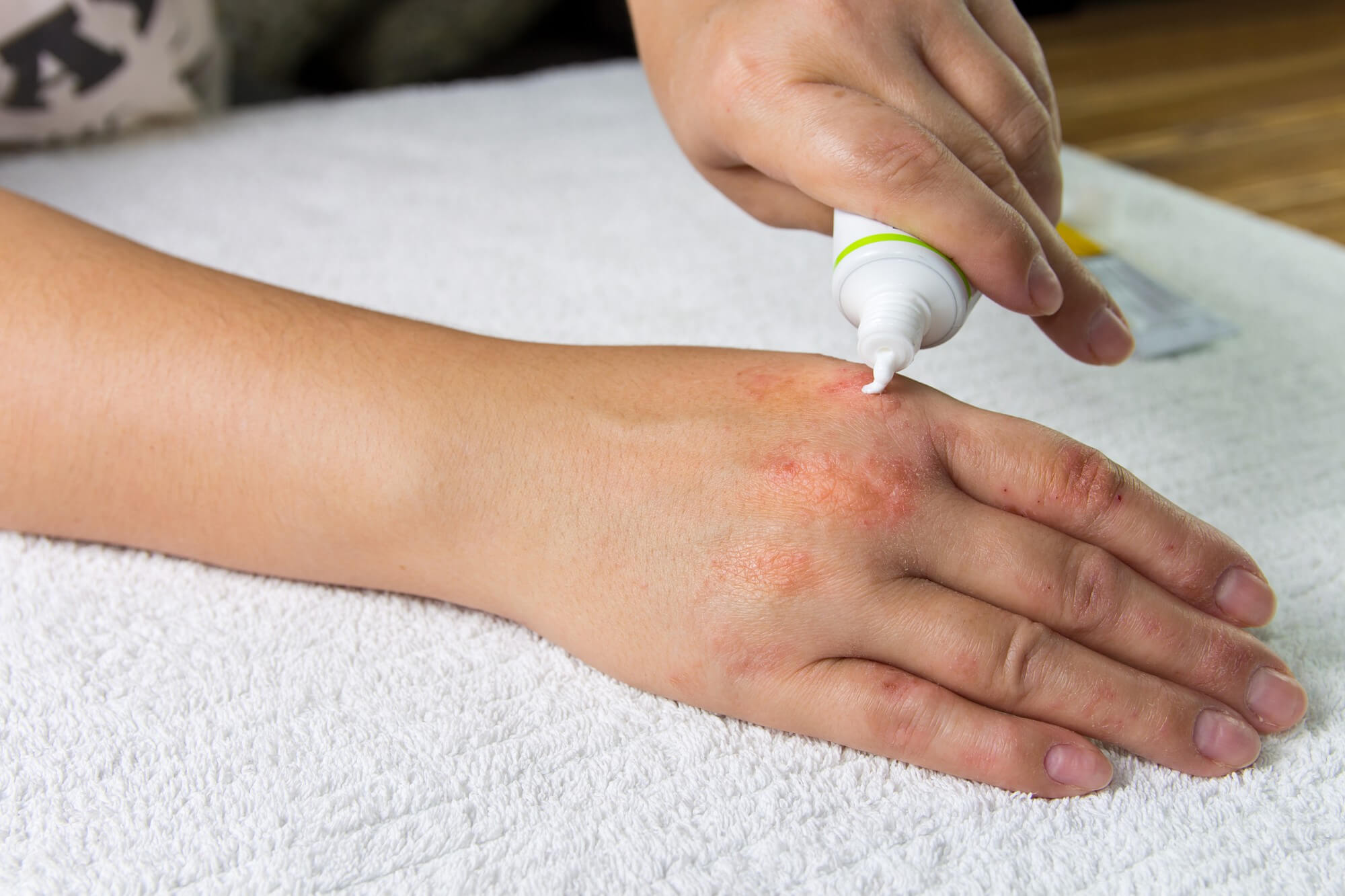
Treatment of microbial eczema includes the use of various medications, including ointments to treat microbial eczema.
Among the most effective medications are ointments containing antibiotics, such as Fusiderm, Bactroban, and erythromycin ointment.
If there is significant inflammation, corticosteroid ointments such as hydrocortisone ointment, Advantan may be prescribed.
If there is severe itching, preparations containing antihistamine components may be used.
Skin care
Good skin care plays a key role in the treatment of microbial eczema. It is recommended to use mild cleansers and moisturizers, avoid excessive moisture and dry skin and avoid contact with irritants.
Avoiding triggers and prevention
It is important to avoid factors that may trigger an exacerbation of microbial eczema, including stress, contact with allergens, and improper diet. Prevention includes good hygiene, a healthy lifestyle and regular check-ups with your doctor.
In conclusion, we would like to note that microbial eczema is a serious disease that requires a careful approach to treatment. However, with the right therapy and adherence to all the doctor's recommendations, most patients can achieve a significant improvement in their skin condition and quality of life.
New materials
Popular Articles
We recommend reading
Contact us in the Contact Us section to ask questions, offer ideas, or for more information about our allergy resource.
Our articles are your trusted source of allergy knowledge. Learn how to make life with allergic reactions easier on our specialized portal.
©
Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
© Lechenie-Allergii.com. All rights reserved.
The information on this site is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. We recommend consulting with qualified medical professionals for accurate information and advice.
 English
English  Українська
Українська  Русский
Русский